- What is a Literature Review?
- The Purpose of Literature Reviews
- Guidelines for Writing a Literature Review
- How to Organize a Literature Review?
- Software for Literature Reviews
- Using Artificial Intelligence for Literature Reviews
- How to Conduct a Literature Review?
- Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in a Literature Review
- Methods for Literature Reviews
- What is a Systematic Literature Review?
- What is a Narrative Literature Review?
- What is a Descriptive Literature Review?
- What is a Scoping Literature Review?
- What is a Realist Literature Review?
- What is a Critical Literature Review?
- Meta Analysis vs. Literature Review
- What is an Umbrella Literature Review?
- Differences Between Annotated Bibliographies and Literature Reviews
- Literature Review vs. Theoretical Framework
- How to Write a Literature Review?
- How to Structure a Literature Review?
- How to Make a Cover Page for a Literature Review?
- How to Write an Abstract for a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Introduction?
- How to Write the Body of a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Conclusion?
- How to Make a Literature Review Bibliography?
- How to Format a Literature Review?
- How Long Should a Literature Review Be?
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- How to Present a Literature Review?
- How to Publish a Literature Review?
What is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic that provides an overview of current knowledge. It analyzes, synthesizes, and critically evaluates existing research to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on a subject. A good literature review doesn’t just summarize scholarly sources. It identifies research gaps and provides an overview of current knowledge, relevant theories, and methods.

Researchers can write standalone papers based solely on comprehensive literature reviews, summarizing existing research and suggesting directions for further research. More often, literature reviews are included at the beginning of empirical studies to establish a foundation for data collection and analysis. Literature reviews are necessary when writing a thesis, dissertation, or research paper, as they situate research within existing knowledge. Writing literature reviews is a key skill for graduate school or research careers. Such reviews help in understanding the broader context of a research topic and identifying where your research fits into the existing body of work.
There are different methods to conduct a literature review. The most common are systematic, narrative, scoping, meta-analyses, realist, and umbrella reviews. Even though it is not a literature review method per se an annotated bibliography also plays a role when writing a literature review. Some literature reviews critically evaluate the key findings of journal articles while others just focus on key themes or describe the literature without critically analyzing it.
When writing a literature review section, it is important to draw connections among multiple sources and focus on synthesizing insights into a coherent narrative or series of arguments. In this literature review guide, we will outline some recommended steps you can follow to conduct an effective literature review.
How to conduct a literature review?
One of the first steps when conducting a literature review is to refine a clear topic and research question to guide your literature search. Ensure your research question is specific, focused, and relevant to your field of study. This helps streamline the literature review writing process and makes it easier to find relevant literature. Once you have identified your research question, determine the focus of your literature review by deciding on its breadth and depth, ensuring it aligns with your research process. Justify your choices of sources, which may include scholarly books, journal articles, dissertations, conference papers, and grey literature, based on their relevance to your research question.
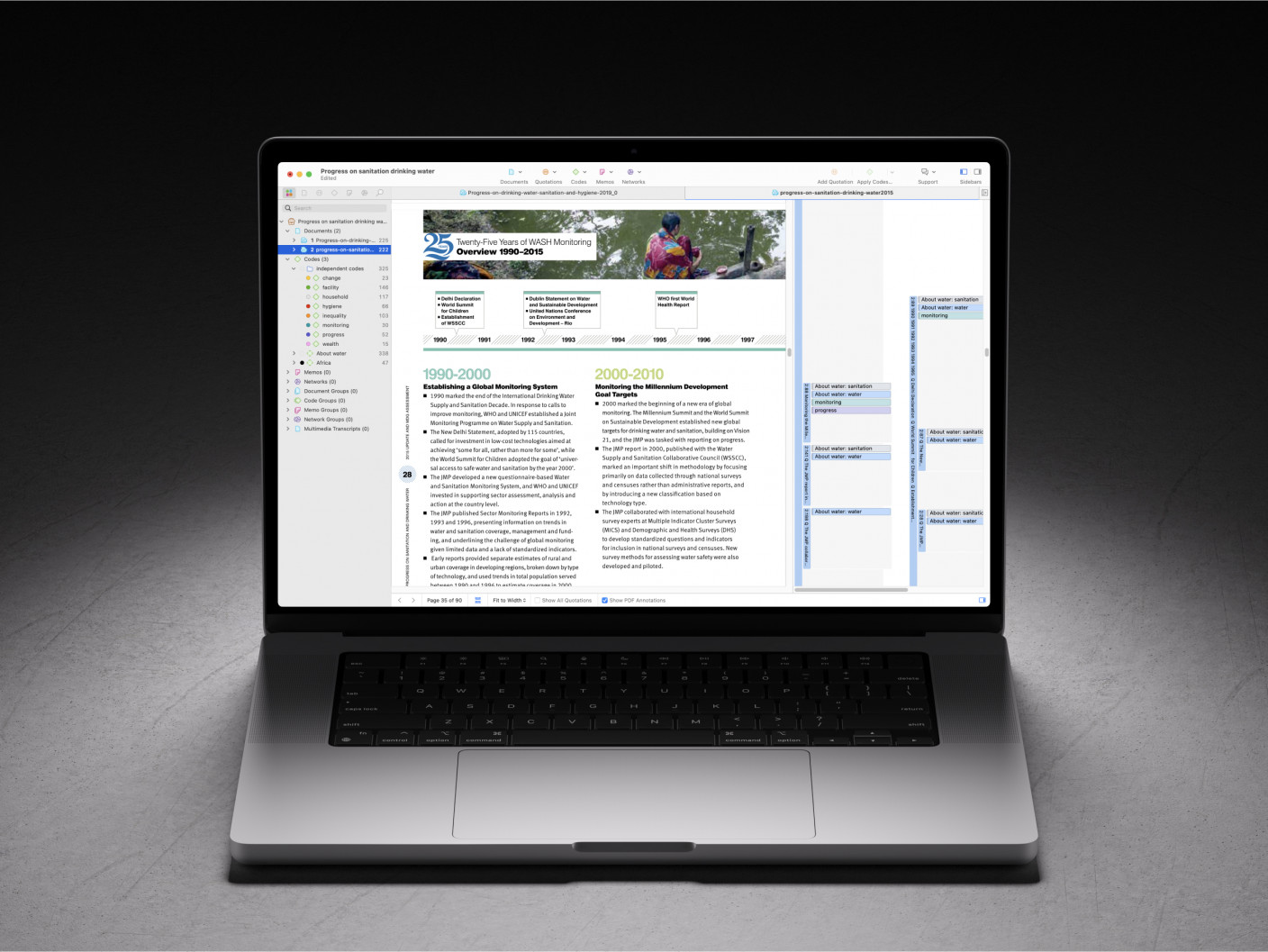
After your research question and focus have been established, it is time to move on to the literature search. To conduct a comprehensive literature search, use multiple sources like scholarly books, journal articles, and dissertations, and utilize citation management tools to organize your references. Incorporate grey literature, such as reports and policy documents, and use both keyword searching and citation searching across various databases to ensure thorough coverage of relevant literature and identify influential studies and emerging trends. Consider using ATLAS.ti Web which, with its integrated Paper Search 2.0 tool, allows you to search, import, and analyze literature from Semantic Scholar, enhancing your ability to manage and review a wide array of sources.
Once you have gathered the relevant literature, conduct a critical analysis to explore relationships, major themes, and gaps in the research. Analyze the methodological approach, and the relationship of each source to other works. Use a comprehensive list of questions to guide your analysis.
Critical evaluation involves assessing the quality and relevance of each source. Consider the authority of the authors: Are they recognized experts in the field? Review highly cited studies in your area to ensure you understand influential contributions to the scholarly conversation around your topic. Evaluate how current the research is by asking questions such as: Is it up-to-date, or have more recent studies superseded it? More recently published studies are typically more compelling, but you may also find it valuable to include key historical papers that have shaped your understanding of your research topic.
Assess the coverage of each source: Does it provide a comprehensive overview of the topic, or does it focus on a narrow aspect? Reading papers that provide a thorough review of the literature can help you familiarize yourself with current understanding and unanswered questions, while more focused papers can provide deeper insights into specific aspects of your research topic.
Examine the methodology used in each study. Verify if the methods are appropriate for the research questions being addressed or if there are limitations that might affect the results. Finally, consider how each source relates to other works in the field. Does it support, challenge, or build upon previous research? Use these questions to develop a critical and nuanced understanding of the literature. Ultimately, your critical evaluation of the literature will form the building blocks of your arguments for why your particular study contributes something novel and interesting to scholarly conversation.
Identifying gaps in existing research is crucial to informing your own research question. Look for main points and recurring central themes in the literature to organize your review effectively. Use your analysis to inform your research methods and design. Gaps in the body of research represent areas where knowledge is lacking or where existing studies have produced conflicting results. Identifying these gaps can help you define the contribution of your own research. To find gaps, look for questions that have not been answered or areas where current knowledge is limited. Consider whether there are any inconsistencies or contradictions in the literature that need to be resolved.

What are the different kinds of literature reviews?
Literature review methods are crucial in academic research, helping to synthesize existing knowledge, identify research gaps, and guide future studies. These methods cater to different research needs and contexts, providing comprehensive insights into the literature on specific topics.
Systematic literature reviews
Systematic reviews follow a rigorous and predefined protocol to provide a comprehensive summary of evidence on a particular topic. They ensure transparency, reproducibility, and are valuable for evidence-based decision-making, especially in fields like healthcare and social sciences.
Narrative literature reviews
Narrative reviews offer a qualitative summary and interpretation of literature on a specific topic. They are more flexible and less structured than systematic reviews, making them useful for exploring new or emerging topics.
Meta-analysis literature reviews
This method statistically combines results from multiple studies to derive a precise understanding of a field or issue. It enhances statistical power and resolves uncertainties from individual studies, providing high-level evidence, which is particularly valuable in healthcare research.
Umbrella literature reviews
Umbrella reviews compile evidence from multiple systematic reviews and meta-analyses on a specific topic. They synthesize high-level evidence, offering a comprehensive overview of research, though the quality of included reviews can affect the findings.
Descriptive literature reviews
Descriptive reviews aim to summarize the current state of knowledge on a topic without the stringent criteria of systematic reviews. They provide a broad overview, identifying patterns, themes, and gaps in the literature.
Scoping literature reviews
Scoping reviews provide a preliminary assessment of the size and scope of available research on a topic. They help map out the literature and identify gaps, aiding in refining research questions.
Critical literature reviews
Critical reviews involve detailed analysis and critique of existing literature, challenging assumptions and opening new research avenues. They offer in-depth analysis and critical insights.
Realist literature reviews
These theory-driven reviews focus on understanding how and why interventions work in specific contexts. They aim to develop and refine program theories, explaining the mechanisms behind an intervention's success or failure.
Different literature review methods serve various research purposes and needs. Choosing the appropriate method is crucial for aligning with research questions and goals, ensuring the review contributes meaningfully to the field. Each type of literature review, from systematic and narrative reviews to meta-analyses and critical reviews, offers unique strengths and applications, making them indispensable methods in academic research.
When reviewing literature for a research paper, understanding the distinct methodologies of each literature review is vital. For instance, systematic reviews offer a thorough analysis crucial for theoretical scholarship, while narrative reviews provide context and depth, beneficial for engaging with cultural sources,theoretical frameworks, and other potentially broader sources that are relevant to the research topic.
Including an annotated bibliography can also be beneficial, as it helps to track key sources and their relevance to your research paper. Engaging with peer-reviewed articles and scholarly articles is essential to ensure the credibility and depth of your research process. This engagement allows you to contribute meaningfully to key debates and build upon the work of other researchers. Understanding these methods and their applications can significantly enhance the quality and impact of your writing a literature review.
How to write a literature review?
Writing a literature review of a particular topic requires a clear structure and a thorough understanding of key concepts. Start by organizing the body of your review in chronological order or according to a specific theoretical approach. Gather and synthesize recent studies and other sources from different disciplines, ensuring well-structured paragraphs that provide a comprehensive summary and critical evaluation. Highlight your own interpretations while maintaining a balanced consideration of all relevant viewpoints. The introduction should outline the review's scope and significance, explain the relevance of the topic, and provide necessary background information.
In the body, organize your sources thematically, chronologically, or methodologically, and critically analyze the literature. Address recurring themes, evaluate research methods and key concepts, and highlight gaps your research aims to fill. Conclude by summarizing key findings, discussing implications for your research, and identifying areas for future studies. Ensure your review is coherent and logically organized, with consistent citations of resources and publications. This approach helps researchers understand the current state of research and identify areas for further study, making your article a significant contribution to the field.
A well-written literature review demonstrates your grasp of the topic and contributes new knowledge. Read widely, take detailed notes, and be rigorous in your evaluation. Use feedback from peers to identify areas for improvement. Stay focused on your research question, avoid unnecessary information, and ensure your review is comprehensive yet concise. By meticulously analyzing existing literature, you provide valuable insights that support your research. This helps create a strong foundation for your study and advances understanding in your field.
The guide to literature reviews
A literature review is a critical component of academic research, providing a comprehensive overview of existing knowledge on a particular topic. By meticulously analyzing and synthesizing previous studies, a literature review not only contextualizes your research within the broader field but also identifies gaps that your work aims to address. This process involves gathering sources from various disciplines, organizing them coherently, and critically evaluating their contributions. Understanding what a literature review entails and how to effectively write one is essential for producing high-quality, impactful research. Through careful planning, thorough research, and clear organization, you can create a literature review that significantly enhances the depth and quality of your study.
We have created this guide to offer you a foundational understanding of the basics of literature reviews and some of the software and different techniques available to researchers. We have divided this guide into different sections as outlined below. Whether this is your first literature review or you are just curious about different methods, we recommend reading this guide to learn more about literature reviews, the different tools you can use and how literature reviews are used in different industries.
Introduction to literature reviews
Literature review basics
Useful tools in literature reviews
Types of literature reviews
- Methods for literature reviews
- Systematic literature reviews
- Narrative literature reviews
- Descriptive literature reviews
- Scoping literature reviews
- Realist literature reviews
- Critical literature reviews
- Meta-analysis vs literature reviews
- Umbrella literature review
- Annotated bibliography vs literature reviews
- Theoretical frameworks vs literature reviews
Writing a literature review
- How to write a literature review?
- Literature review structure
- Literature review cover page
- Literature review abstract
- Literature review introduction
- Literature review body
- Literature review conclusion
- Literature review bibliography
- Literature review format
- Literature review length
- Examples of literature reviews
- Literature review presentations
- Publishing a literature review