- What is a Literature Review?
- The Purpose of Literature Reviews
- Guidelines for Writing a Literature Review
- How to Organize a Literature Review?
- Software for Literature Reviews
- Using Artificial Intelligence for Literature Reviews
- How to Conduct a Literature Review?
- Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in a Literature Review
- Methods for Literature Reviews
- What is a Systematic Literature Review?
- What is a Narrative Literature Review?
- What is a Descriptive Literature Review?
- What is a Scoping Literature Review?
- What is a Realist Literature Review?
- What is a Critical Literature Review?
- Meta Analysis vs. Literature Review
- What is an Umbrella Literature Review?
- Differences Between Annotated Bibliographies and Literature Reviews
- Literature Review vs. Theoretical Framework
- How to Write a Literature Review?
- How to Structure a Literature Review?
- How to Make a Cover Page for a Literature Review?
- How to Write an Abstract for a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Introduction?
- How to Write the Body of a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Conclusion?
- How to Make a Literature Review Bibliography?
- How to Format a Literature Review?
- How Long Should a Literature Review Be?
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- How to Present a Literature Review?
- How to Publish a Literature Review?
How to Conduct a Literature Review?
Conducting a proper literature review is essential for understanding the breadth of research studies in any field. This process involves evaluating research methodologies and findings to assess how different approaches contribute to our knowledge. A critical assessment of published literature is necessary to identify key works and their relevance to your central research question. To conduct a literature review effectively, define a specific research question then carefully examine abstracts to determine which studies are relevant for your research. Then, as you read each article, take meticulous notes on each research study, paying close attention to conflicting studies and gaps in the research.

Research funded by other institutions or governing bodies might be motivated by a particular research problem. However, the literature review is still important for providing a robust foundation upon which the researchers can build.
A comprehensive literature review synthesizes findings into a coherent narrative representing a larger paper's background. It can involve analyzing significant research studies, funded projects, and loosely related studies to provide a thorough understanding of the topic. This process helps identify where more research is needed and frames the thought processes behind the research questions.
Ultimately, a well-conducted literature review supports your qualitative research paper and contributes to the academic community by mapping out the current state of knowledge and highlighting areas for further questions and investigation. Literature reviews are also valuable tools for other researchers who need to find a summary of the field of knowledge.
Defining your research scope
Identify your research question
An important step in all literature reviews is to define your research scope. This is typically done by formulating a specific research question, which will guide the focus and scope of your literature review. A well-defined research question helps avoid dead-end searches by ensuring that worthwhile studies can identified across multiple databases and that relevant sources are included in the search strategy. For any research project, having a central research question is essential. It is important to aim for comprehensiveness in your review, and having a concrete research question in mind can help you determine when you have reviewed enough articles to build a solid foundation for your research.
The research question forms the backbone of your literature review. It shapes the direction of your research and helps you stay focused on the relevant topics. A clear research question also aids in setting boundaries for your literature review, ensuring that you do not stray into unrelated areas. To formulate a research question, consider the main issues or problems within your area of interest. Reflect on what you aim to discover or understand through your research. A specific and well-defined research question will guide your literature search and analysis, making the review process more manageable and effective.

Determine the focus of your literature review
Once you have identified your research question, determine the focus of your literature review. This involves deciding on the breadth and depth of the review. Establish the significance of your research by showing that you have examined the breadth of knowledge and can justify your thesis or research questions.
To determine the scope, consider the comprehensiveness of your review. Will you include all available studies on your topic, or will you focus on a specific subset of literature? Clearly establishing the concepts, theories, or phenomena you are interested in can help you decide the scope of your specific study. Are you looking at the most recent studies, or do you need to include historical perspectives as well? Your literature review's scope should align with your research goals and objectives. It should also be feasible given the time and resources available for your project.
The scope of your review will also influence the type of sources you include. Scholarly books, journal articles, dissertations, and conference papers are common sources for literature reviews. Depending on your topic, you might also include grey literature such as reports, policy documents, and working papers. Be sure to justify your choices and explain why certain types of literature are relevant to your research question.
Searching for and evaluating literature
Conducting a comprehensive literature search
To conduct a comprehensive literature search, use multiple sources such as scholarly books, journal articles, and dissertations. Utilize citation management tools such as Zotero, Mendeley, or CAQDAS such as ATLAS.ti to keep track of your sources and citations. Conducting literature reviews is how researchers engage in scholarly conversation around a topic, so being aware of what others found and how their contributions are interconnected can help you understand and join this conversation. Also, consider searching for grey literature, which includes reports, policy documents, and other non-peer-reviewed materials. Grey literature can provide valuable insights, especially in fields where research is rapidly evolving.
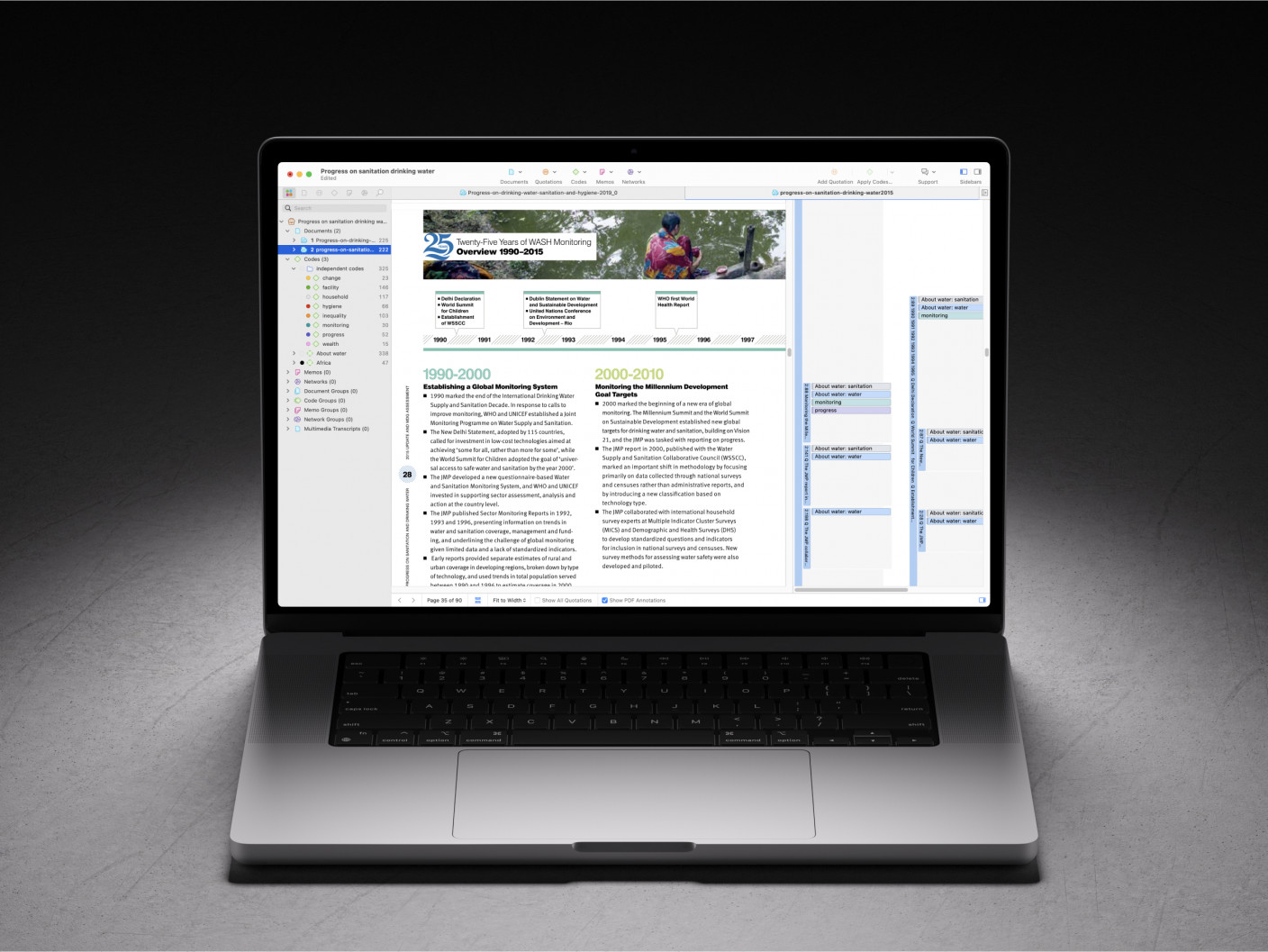
A comprehensive literature search involves more than just finding articles; it requires a strategic approach to ensure that you cover all relevant literature. Start by identifying key terms and phrases related to your research question. Use these terms to search databases and online libraries. Make sure to search broadly, including different types of sources and databases. For instance, you might use PubMed for medical literature, IEEE Xplore for engineering papers, and JSTOR for humanities research. If you use ATLAS.ti Web for your research project, the integrated Paper Search tool allows you to easily search for, import, and analyze literature straight from Semantic Scholar, which is a database that houses over 200 million articles across various research areas.
In addition to keyword searching, use citation searching to track how scholars have cited and built upon key works in your field. This can help you identify influential studies and emerging trends.
Critically evaluating and analyzing the literature
Once you have gathered the relevant literature, conduct a critical analysis to explore relationships, major themes, and gaps in the research. Analyze the authority, coverage, methodology, and relationship of each source to other works. Use a comprehensive list of questions to guide your analysis.
Critical evaluation involves assessing the quality and relevance of each source. Consider the authority of the authors: Are they recognized experts in the field? It is important to review highly cited studies in your area to ensure you understand influential contributions to scholarly conversation around your topic. Evaluate the currency of the research: is it up-to-date, or have more recent studies superseded it? More recently published studies are typically more compelling, but you may also find it valuable to include key historical papers that have shaped your understanding of your research topic. Assess the coverage of each source: does it provide a comprehensive overview of the topic, or does it focus on a narrow aspect? Reading papers that provide a thorough review of the literature can be a great help to familiarize yourself with current understanding and unanswered questions, while more focused papers can provide deeper insights into specific aspects of your research topic.
Examine the methodology used in each study. Verify if the methods are appropriate for the research questions being addressed or if there are limitations that might affect the results. Finally, consider how each source relates to other works in the field. Does it support, challenge, or build upon previous research? Use these questions to develop a critical and nuanced understanding of the literature. Ultimately, your critical evaluation of the literature will form the building blocks of your arguments for why your particular study contributes something novel and interesting to scholarly conversation.

Identifying gaps and themes in the research
Identifying gaps in existing research is crucial to informing your own research question. Look for themes in the literature to organize your review effectively. Use your analysis to inform your research methods and design.
Gaps in the body of research represent areas where knowledge is lacking or where existing studies have produced conflicting results. Identifying these gaps can help you define the contribution of your own research. To find gaps, look for questions that have not been answered or areas where current knowledge is limited. Consider whether there are any inconsistencies or contradictions in the literature that need to be resolved.
Themes in the literature are recurring topics or patterns that emerge across different studies. Identifying these themes can help you structure your literature review and provide a coherent narrative. Group related studies together and discuss how they contribute to understanding the main themes. Use your analysis of gaps and themes to develop your research design and methodology. This will ensure that your study addresses important questions and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in your field.
Being selective and cautious in your analysis
Select your research studies carefully. Be cautious when using quotes, as they can take up valuable space. Ensure that your analysis provides a clear understanding of the existing research and its implications.
Not all sources are equally relevant or valuable for your literature review. Be selective and choose the most significant and high-quality studies. Avoid including sources that do not directly contribute to answering your research question. When using quotes, ensure they are necessary and add value to your analysis. Paraphrasing can often be more effective and concise.
Your analysis should be thorough, covering all relevant aspects of the literature. Provide a balanced view, acknowledging different perspectives and interpretations. Highlight the strengths and weaknesses of existing research, and discuss the implications for your own study. A well-conducted literature review should provide a clear and critical overview of the current state of knowledge and set the stage for your research.

Online resources and tools for conducting a literature review
Online databases and search engines
Online databases and search engines are invaluable resources for finding relevant literature. We recommend using tools like Google Scholar, PubMed, and other academic databases to locate scholarly articles and books. Online databases provide access to a vast array of scholarly literature. Google Scholar is a popular tool that covers a wide range of disciplines. PubMed is essential for medical and health-related research, while databases like IEEE Xplore are crucial for engineering and technology studies. Use advanced search features to refine your searches and find the most relevant articles. For example, you can filter results by publication date, author, journal, and more. Conducting your literature review in ATLAS.ti Web can streamline your research process and focus on analysis with powerful data exploration tools. ATLAS.ti Web's Paper Search function allows you to search, import, and cite academic resources from Semantic Scholar.
Citation management tools
Citation management tools like Zotero, Mendeley, or some computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software applications (CAQDAS) such as ATLAS.ti help store your articles and track your research citations. These tools can also assist in organizing and structuring your literature review. Citation management tools are essential for keeping track of your sources and citations. They allow you to organize references, create bibliographies, and share research with collaborators. Zotero and Mendeley are user-friendly tools that integrate with word processors, making it easy to insert citations and generate reference lists. CAQDAS tools like ATLAS.ti offer advanced features for qualitative data analysis, including the ability to code and analyze articles.

Organizing and structuring your review
Use online resources and tools to help you organize and structure your review. CAQDAS tools, for example, can compile all your articles, making it easier to manage your research process. Organizing your literature review involves creating a logical structure that guides the reader through your analysis. Start with an introduction that outlines the scope and purpose of your review. Follow this with sections that discuss the main themes and gaps in the literature. Use headings and subheadings to break up the text and make it easier to follow.
Compile tools that can help you organize your review effectively. CAQDAS tools like ATLAS.ti allow you to code and categorize your sources, making it easier to identify themes and patterns. Use citation management tools to keep track of your references and ensure that your citations are accurate and consistent.
Conclusion
The literature review process involves defining your research scope, searching and evaluating literature, and using online resources and tools effectively. By following these steps, you can compile a comprehensive and insightful literature review that represents the background of your research question, addresses research gaps, and informs further research in your field. Start by identifying your research question, conduct a thorough search, critically evaluate the literature, and use the right tools to organize and structure your review. By adhering to these guidelines, you will be well on your way to conducting a literature review that is thorough, well-organized, and insightful, ultimately contributing to the body of knowledge in your field. A well-executed literature review enhances your understanding of the research landscape and provides a solid foundation for your own study. It demonstrates your ability to critically engage with existing research and highlights the significance of your research question within the broader context of the field.
Moreover, a comprehensive literature review can reveal new directions for future research and inform the development of innovative methodologies. It serves as a valuable resource for other researchers, offering a synthesized overview of key findings and debates. By carefully documenting your search process and evaluation criteria, you also ensure the transparency and reproducibility of your review, which are essential aspects of rigorous academic research. Overall, conducting a literature review is a multifaceted process that requires careful planning, systematic searching, critical evaluation, and thoughtful organization. By mastering these skills, you can produce a literature review that not only supports your research objectives but also contributes to the advancement of knowledge in your field. Embrace the challenge and take pride in the valuable insights and contributions your literature review will provide to the academic community.