- What is a Literature Review?
- The Purpose of Literature Reviews
- Guidelines for Writing a Literature Review
- How to Organize a Literature Review?
- Software for Literature Reviews
- Using Artificial Intelligence for Literature Reviews
- How to Conduct a Literature Review?
- Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in a Literature Review
- Methods for Literature Reviews
- What is a Systematic Literature Review?
- What is a Narrative Literature Review?
- What is a Descriptive Literature Review?
- What is a Scoping Literature Review?
- What is a Realist Literature Review?
- What is a Critical Literature Review?
- Meta Analysis vs. Literature Review
- What is an Umbrella Literature Review?
- Differences Between Annotated Bibliographies and Literature Reviews
- Literature Review vs. Theoretical Framework
- How to Write a Literature Review?
- How to Structure a Literature Review?
- How to Make a Cover Page for a Literature Review?
- How to Write an Abstract for a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Introduction?
- How to Write the Body of a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Conclusion?
- How to Make a Literature Review Bibliography?
- How to Format a Literature Review?
- How Long Should a Literature Review Be?
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- How to Present a Literature Review?
- How to Publish a Literature Review?
Software for Literature Reviews
Software and research tools can assist qualitative researchers from the start to the end of a literature review. These tools usually include search engines, reference managers, and other software with multiple functions like computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software (CAQDAS) where researchers can compile references, analyze documents, produce summaries, and organize them. It is up to you to choose the best tools that work better for your research purposes.

Search engines can vary depending on the area of focus or accessibility, for example, some are focused on biomedical and life science literature while others offer access to a broader range of articles. Some popular search engines are free to use with most articles being open-source. However, other search engines have subscription-only articles but have some open-access articles. Search engines for research papers are indispensable tools in the literature review process. These tools streamline literature searches, providing you with vast access to scientific databases.
A reference manager goes hand in hand with search engines. It is a valuable tool because it compiles scientific literature and other existing literature in a single place. You can also export the references as needed and in different formats. Many have a browser extension to facilitate quick access to full-text articles. These tools offer a user-friendly interface and advanced search capabilities, enabling you to manage your research projects efficiently. Choosing a reference manager depends on your budget and preferences.
Computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software are also useful for literature reviews. They can be the go-to source for a researcher to compile notes, articles, and references as they can all be stored in one place. For example, ATLAS.ti Web's Paper Search feature lets you search, import, and cite academic resources from Semantic Scholar. You can then codify and analyze the literature in one place. The platform supports a cohesive and streamlined workflow that facilitates direct citation of imported documents within ATLAS.ti projects. This comprehensive integration allows researchers to conduct their entire literature review process within a single platform, focusing more on analysis and less on administrative tasks.
By integrating these tools into their workflow, researchers can efficiently conduct literature reviews, extract key information, and collaborate effectively with their teams. These powerful tools enhance the quality of research outputs and save valuable time. For any work related to the literature review, from conducting a literature search to a systematic review, these tools can optimize your workflow and ensure thorough analysis of the research published.
Open-source search engines
Google Scholar
Google Scholar is one of the most popular search engines for academic research, and it provides free access and extensive coverage. One of its useful features is the ability to configure it to include access to university libraries, which can significantly broaden search results and provide access to subscription-based content through institutional affiliations. However, the advanced search options are limited, making finding specific information challenging.

PubMed
Pubmed is a widely used search engine that provides free access to various biomedical and life sciences literature. It is run by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). One of its main benefits is its comprehensive indexing, making it easy to find relevant studies, including qualitative research in health-related fields. One of its disadvantages is that it primarily focuses on biomedical and life sciences, which means it has limited coverage of other disciplines.
BASE (Bielefeld Academic Search Engine)
BASE is one of the world's largest search engines specifically designed for academic open-access web resources. BASE was created by Bielefeld University Library in Bielefeld, Germany. It indexes over 240 million documents from over 8,000 content providers, providing a vast repository of academic literature. It carries several humanities and social sciences papers, making it highly suitable for qualitative research.

CORE (COnnecting REpositories)
CORE is an open-source search engine with research outputs from repositories and journals worldwide. It offers free access to millions of open-access research papers, supporting various disciplines, including humanities and social sciences.
Semantic Scholar
Semantic Scholar is an AI-powered research tool developed at the Allen Institute for AI that provides free access and leverages AI to improve search accuracy and relevance. It features citation context, influential citation identification, and paper summarization. It is particularly strong in interdisciplinary fields such as computer science and biomedical research. ATLAS.ti has partnered with Semantic Scholar in the new Paper Search 2.0 feature in ATLAS.ti Web that allows users to seamlessly search, import, and cite academic resources. This integration provides access to over 200 million scientific resources.
Paid-access search engines
ScienceDirect
ScienceDirect, developed and maintained by Elsevier, is a premier search engine designed to access a vast repository of scholarly literature across various scientific disciplines. Launched in 1997, it forms part of Elsevier's suite of digital solutions to support scientific, technical, educational and medical research. While ScienceDirect offers some open-access articles and free sample issues, most of its content requires a subscription or purchase. Many universities, research centers, and libraries provide access through institutional subscriptions. Individual researchers can also purchase or subscribe to specific content if institutional access is unavailable.
Scopus
Managed by Elsevier, Scopus is an abstract and citation database that indexes millions of journal articles, conference proceedings, patents, and more, providing robust search capabilities and advanced analytics tools. One of its key advantages is the ability to track citations and research impact through features like the h-index calculator and author profiles, which help researchers understand the influence and reach of their work. Scopus offers extensive coverage, including over 71 million records from more than 5,000 publishers.

EBSCOhost
EBSCOhost is a powerful online research platform that provides access to various academic databases covering multiple disciplines. Known for its comprehensive and diverse range of content, EBSCOhost includes specialized databases such as SocINDEX, PsycINFO, and Academic Search Premier, which cater specifically to qualitative research needs.
JSTOR
JSTOR is a highly regarded digital library that provides free articles or subscription-based access to an extensive archive of academic journals, books, and primary sources across numerous disciplines. Known for its comprehensive coverage of the humanities and social sciences, JSTOR includes a vast collection of scholarly articles dating back to the 19th century, which makes it a valuable resource for historical and interdisciplinary research.
Other literature discovery and exploration tools
Research Rabbit
Research Rabbit helps researchers discover relevant papers and authors by visualizing connections and relationships between research articles. It provides an interactive, graphical format to aid in finding new and related research.
R Discovery
R Discovery is an AI-powered literature discovery tool that offers personalized recommendations based on user preferences. It curates content from a massive repository of scholarly articles, making it easier to stay updated with the latest research in various fields
Connected Papers
Connected Papers creates a visual graph of related papers, helping researchers identify influential works and discover new connections within a specific research topic.

Litmaps
Litmaps uses citation networks to help discover relevant papers that may be overlooked with traditional keyword searches. Litmaps provides automated alerts for new publications, identifies key authors, highlights research gaps, and allows sharing of findings with others. It is used by a wide range of researchers globally and aims to improve access to scientific sources through its freemium model.
Citation Chaser
Citation Chaser is a tool designed to automate forward and backward citation chasing in academic research. It uses the Lens.org API to identify all articles cited by a given set of papers (backward chasing) and all articles that cite those papers (forward chasing). Citation Chaser outputs results in RIS format, which can be easily integrated into reference management systems for further screening and analysis.
EndNote
EndNote is a reference manager and literature review tool widely used in academia for managing research papers and systematic reviews. It allows users to organize references, create bibliographies, and collaborate with colleagues. EndNote offers a subscription-based model, making it a robust choice for in-depth research and systematic reviews. It offers extensive customization options, integration with Microsoft Word, and advanced bibliographic management features.
Mendeley
Mendeley is a reference manager and academic social network that helps researchers organize their research papers and literature reviews. It offers both a free version and premium options, providing cloud storage for PDFs and other research documents. Mendeley also includes a browser extension for easy citation management, making it an essential tool for managing systematic reviews and other research tasks.
Zotero
Zotero is a free reference management tool that helps users collect, organize, cite, and share research papers. It has useful integrations with web browsers and Microsoft Word, allowing users to save references directly from web pages and easily insert citations and full bibliographies in their write-ups, making it an excellent tool for literature reviews and systematic reviews. Zotero is helpful for managing and organizing references efficiently, with its free version being particularly appealing to researchers on a budget. Zotero is a highly versatile open-source reference manager with robust browser integration and optional paid storage for larger libraries.

RefWorks
RefWorks is a web-based reference management service used to manage citations and create bibliographies. It is a subscription-based tool popular in academic libraries and offers features for collaboration and document sharing.
JabRef
JabRef is an open-source reference manager that uses BibTeX as its native format, making it popular among LaTeX users for managing references and generating bibliographies.
BibDesk
BibDesk is a free reference management tool for macOS that integrates with LaTeX. It allows users to organize and manage bibliographic information, making it a useful tool for systematic reviews and literature reviews. BibDesk is particularly useful for users who work extensively with LaTeX documents.

Computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software (CAQDAS)
Computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software (CAQDAS) can summarize scholarly content such as publications and PDF files, make document groups, with advanced features with collaboration features, and review and summarize scholarly literature. It can also use machine learning with a few clicks. While these tools were originally designed to facilitate qualitative data analysis, they are equally valuable for managing and analyzing vast amounts of literature, making CAQDAS a powerful tool for literature reviews.
ATLAS.ti
ATLAS.ti is known for its intuitive and user-friendly interface, making it a popular choice among qualitative researchers. It offers robust tools for data coding, visualization, and network analysis. ATLAS.ti supports various data formats, including text, multimedia, and geographic data. Key features include advanced coding options, sophisticated visualization tools (such as word clouds and networks) and the ability to handle large datasets. It also supports collaborative work, making it suitable for research teams.
Researchers can import their references from their preferred bibliography manager into ATLAS.ti Windows and Mac. Researchers frequently start with references organized in software such as Zotero or EndNote. ATLAS.ti allows for the import of data from these programs using EndNote XML files or BibTeX files. It enables the transfer of references from almost any reference management software.
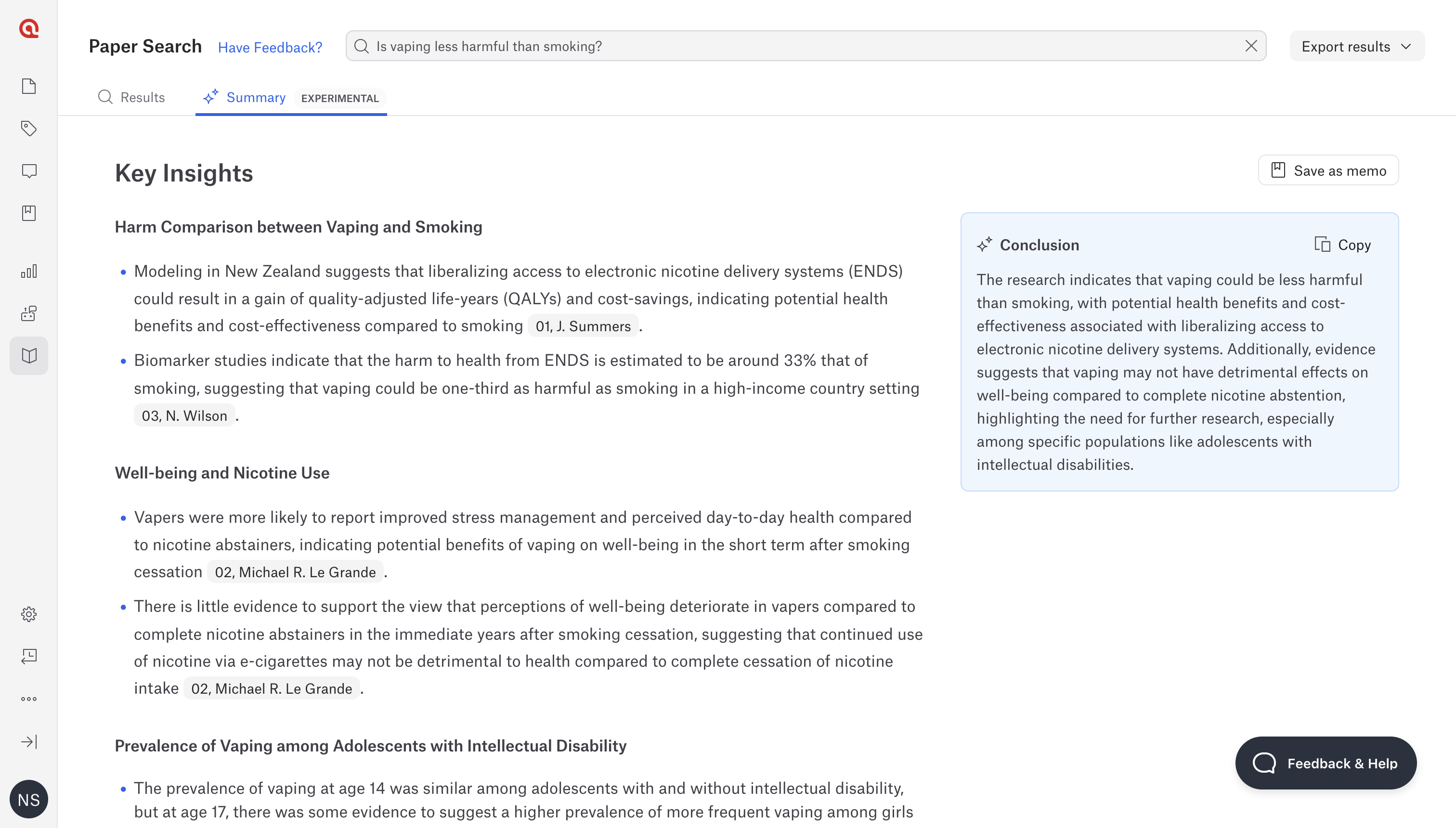
Paper Search 2.0 in ATLAS.ti Web is a state-of-the-art AI tool designed to optimize research workflows by rapidly evaluating the relevance of scientific papers. Researchers input their questions, and the tool conducts extensive searches, providing concise summaries of the most pertinent papers. This technology significantly reduces the time and effort needed, allowing researchers to focus on deeper analysis.
With access to over 200 million scientific resources from Semantic Scholar, Paper Search 2.0 offers a vast database for relevant studies. The streamlined search function efficiently identifies and imports key scientific resources. The AI delivers focused summaries of the top five papers, highlighting content that directly answers the research question. Additionally, it facilitates easy citation within ATLAS.ti projects, ensuring a cohesive workflow.
Supporting the entire literature review process on one platform, the tool uses advanced Natural Language Processing to fully understand research needs, delivering highly relevant search results and summaries. When users input their questions, the AI refines them, generates relevant keywords, and searches the Semantic Scholar database for pertinent papers. It then summarizes the findings and provides actionable insights. This AI-driven functionality, developed by the ATLAS.ti AI Lab, transforms raw data into valuable knowledge, streamlining the literature review process. Future updates will expand database access, refine search capabilities, and integrate advanced AI features for deeper insights.