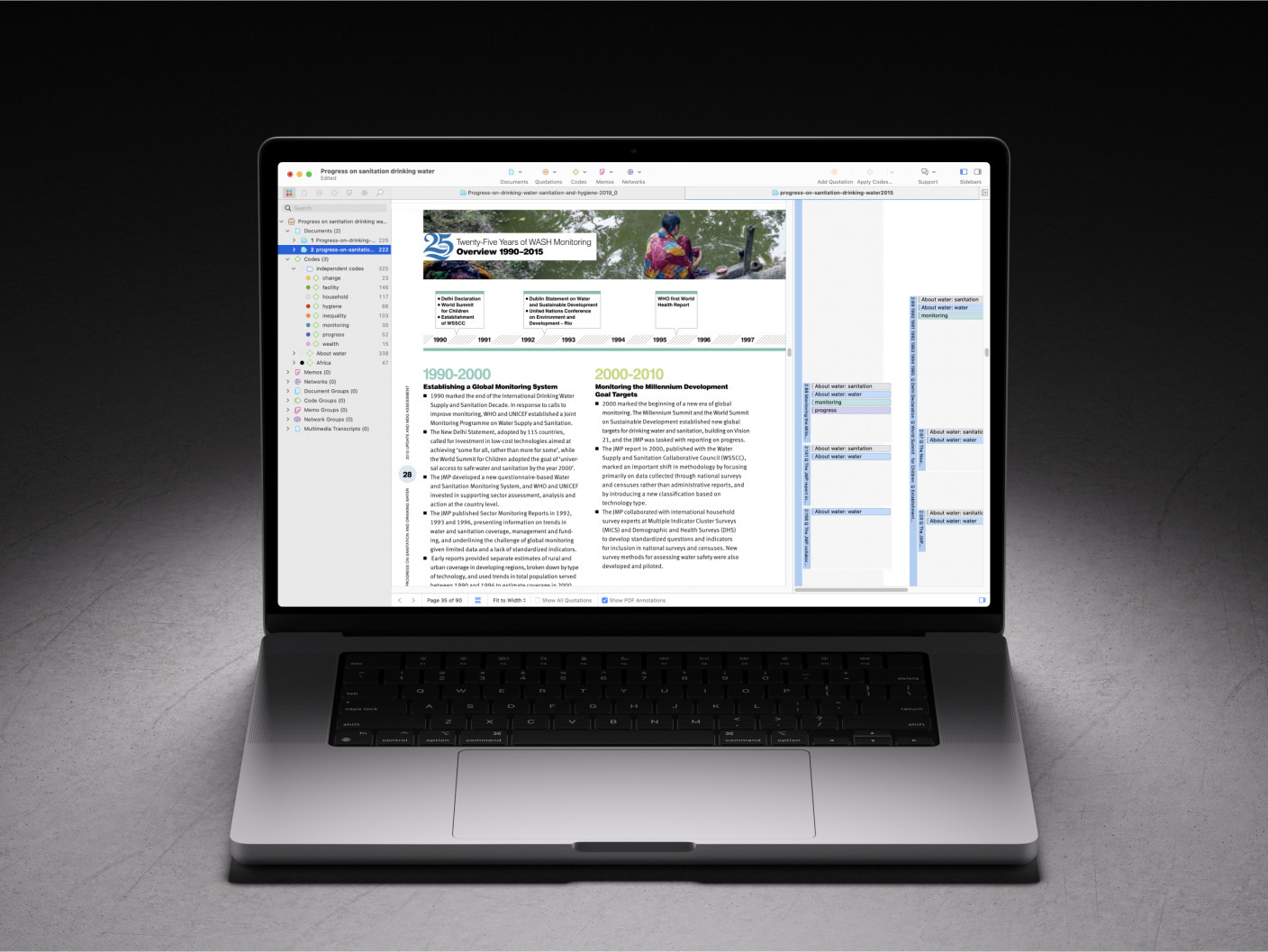
- What is a Literature Review?
- The Purpose of Literature Reviews
- Guidelines for Writing a Literature Review
- How to Organize a Literature Review?
- Software for Literature Reviews
- Using Artificial Intelligence for Literature Reviews
- How to Conduct a Literature Review?
- Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in a Literature Review
- Methods for Literature Reviews
- What is a Systematic Literature Review?
- What is a Narrative Literature Review?
- What is a Descriptive Literature Review?
- What is a Scoping Literature Review?
- What is a Realist Literature Review?
- What is a Critical Literature Review?
- Meta Analysis vs. Literature Review
- What is an Umbrella Literature Review?
- Differences Between Annotated Bibliographies and Literature Reviews
- Literature Review vs. Theoretical Framework
- How to Write a Literature Review?
- How to Structure a Literature Review?
- How to Make a Cover Page for a Literature Review?
- How to Write an Abstract for a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Introduction?
- How to Write the Body of a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Conclusion?
- How to Make a Literature Review Bibliography?
- How to Format a Literature Review?
- How Long Should a Literature Review Be?
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- How to Present a Literature Review?
- How to Publish a Literature Review?
How to Write a Literature Review?
A literature review is integral to academic research, serving as a pillar for understanding and contextualizing your study within the broader field. The importance of a literature review cannot be overstated, as it demonstrates your grasp of existing research and highlights the contributions and gaps that your work aims to address. By meticulously analyzing and synthesizing existing literature, you provide a comprehensive overview that informs and strengthens your research.

Literature reviews come in various forms and serve different purposes depending on the research study. Sometimes, a literature review serves as an introduction to a larger research paper or thesis. This type of review sets the stage for your study by summarizing existing research, identifying gaps, and establishing the relevance of your research question. It provides the necessary background that supports your hypothesis and justifies the need for your study.
In other instances, a literature review may be a standalone paper, dedicated entirely to summarizing and critically evaluating existing research on a particular topic. This form of literature review is common in fields where a comprehensive understanding and synthesis of existing knowledge are necessary. Standalone literature reviews are valuable for identifying trends, evaluating methodologies, and suggesting areas for future research. They serve as authoritative sources that scholars and practitioners can reference to gain insights into the current state of research on a specific topic.
Regardless of the type, a well-written literature review requires careful planning, thorough research, and clear organization. It involves identifying relevant literature, summarizing key findings, critically evaluating the studies, and presenting the information coherently and logically.
How to write a literature review? Step-by-step guide
When writing literature reviews, it is essential to follow a structured sequence to ensure clarity, coherence, and thorough analysis. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the reviewing literature process effectively:
Body
Write the body of the literature review first. This is where you gather, summarize, and synthesize the research findings from relevant articles, scholarly articles, and cultural sources theoretical. Organize your sources by themes, chronology, or methodology, and critically analyze the literature. Ensure your literature review writing includes well-structured paragraphs and addresses recurring central themes. Critically evaluate the research methods and key concepts, providing a coherent whole analysis of the literature related to your research topic. This section should show your understanding of the existing literature and highlight the gaps your research aims to fill.
Introduction
Next, you can write the introduction. After you have a good grasp of the content from writing the body, you can effectively introduce the topic, provide necessary background information, state the research question and explain the significance of the review. This section should set the stage for the literature review section and contextualize your literature search within the broader field. Mention how most research papers rely on a thorough literature review to establish a foundation.
Conclusion
Write the conclusion after the body and introduction are complete. Summarize the key findings from the body, reiterate the importance of the topic, discuss the implications for your own research, and suggest areas for further research. Highlight how your literature review contributes to understanding the research topic and what future studies could explore. This is where you emphasize the need for further research based on the gaps identified in the literature.
Abstract
The abstract is usually written last and it is a concise summary of your entire literature review, so it is easiest to write once all other sections are complete. Include the main themes or trends discussed, the scope of the literature reviewed, and a brief statement of your conclusions. This will provide a snapshot of your literature review for readers.
Bibliography
Compile your reference list as you go, but finalize it after completing the main sections of your literature review to ensure all sources are correctly cited and formatted according to the required citation style. Include an annotated bibliography if needed, summarizing and evaluating each source. This section is crucial for acknowledging other researchers and providing readers with a trail to follow for their own literature search. Ensure you have relevant sources and that the bibliography is comprehensive and well-organized.
Important tips when writing a literature review
Writing a literature review can be a daunting task, but by following some essential tips, you can create a coherent, insightful, and well-organized review. Here are some useful strategies to guide you through the process:
Define your research purpose
Understanding the purpose of your literature review is crucial. Clearly articulate what you aim to achieve. Whether it’s to provide an overview of the current state of research, identify gaps, or support your own research, having a clear purpose will guide your writing and ensure you stay focused.
Organize your sources
Before diving into writing, organize your sources. Group them by themes, methodologies, or chronologies. This will help you create a logical structure for your review and make it easier to draw connections between different studies.
Use a clear structure
A well-structured literature review typically includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. In the introduction, set the stage by explaining the scope and purpose of your review. The body should discuss the sources in a structured manner, while the conclusion summarizes the key findings and their significance.
Summarize and synthesize
Summarize the main points of each source, but also synthesize the information to show how the sources relate to each other. Highlight common findings, differences, and gaps in the literature. This synthesis will demonstrate your understanding of the field and how the studies interconnect.
Critically evaluate
Go beyond mere summarization and critically evaluate the sources. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies and their methodologies. This critical evaluation shows your analytical skills and a deep understanding of the topic, providing valuable insights for your readers.

Be objective
Maintain an objective tone throughout your review. Present different perspectives without personal bias. Being objective enhances the credibility of your review and shows that you have thoroughly considered all relevant research.
Use transitions
Ensure your review flows logically by using transition words and phrases. This will help connect your ideas and make it easier for the reader to follow your argument. Good transitions enhance the overall coherence of your review.
Cite your sources
Properly cite all the sources you reference in your review. Use a consistent citation style as required by your field or assignment guidelines. Accurate citations not only give credit to original authors but also strengthen your review’s academic integrity.
Consider writing annotations
Creating an annotated bibliography can be a valuable tool for organizing your sources and synthesizing the information. Summarize each source’s main points and critically analyze how they contribute to your research. An annotated bibliography can enhance your ability to identify gaps and establish a clear direction for your research.
Paraphrase
Instead of relying heavily on direct quotes, paraphrase the information from your sources. Paraphrasing demonstrates your understanding and allows you to integrate the information smoothly into your review, maintaining your unique voice.
Revise and edit
After completing your draft, take time to revise and edit. Look for clarity, coherence, and conciseness. Check for grammatical errors and ensure that your citations are accurate. Editing is a crucial step in producing a polished and professional literature review.
Seek feedback
If possible, seek feedback from peers or mentors. They can provide valuable insights and help you improve your review. Constructive feedback can highlight areas you might have overlooked and enhance the quality of your final draft.
Stay current
Include the most recent research on your topic to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of knowledge. Staying current ensures your review is relevant and reflects the latest developments in your field.
By following these tips, you can write a well-structured and insightful literature review that effectively summarizes and evaluates the existing research on your topic. This approach will not only make your review more engaging and informative but also enhance your credibility as a researcher.
Common errors when writing literature reviews
When writing a literature review, it is easy to make certain common errors that can undermine the quality of your work. One common mistake is a lack of focus. Ensure your literature review has a clear focus and is not too broad. The narrower your topic, the more in-depth your review can be. This specificity allows you to provide a detailed analysis of the selected studies and avoid being overwhelmed by the sheer volume of available research.
Insufficient critical evaluation is another frequent issue. Simply summarizing sources is not enough. You need to critically evaluate the literature, comparing and contrasting different studies and identifying strengths, weaknesses, and gaps. This critical analysis demonstrates your understanding of the topic and your ability to engage with the existing research.
Poor organization can also detract from the effectiveness of your literature review. Organize your review logically, using headings and subheadings to guide the reader and ensure each section flows smoothly into the next. A well-structured review is easier to follow and more persuasive.
Inconsistent citation style is a common error that can confuse readers and detract from the professionalism of your review. Be consistent with your citation style throughout your review, ensuring all sources are properly cited to avoid plagiarism. This consistency makes it easier for readers to locate your sources.
Conclusion
A good literature review helps refine your research question, identifies key concepts, and ensures that you are building on a solid foundation of existing knowledge. By gathering and analyzing peer-reviewed articles and other credible sources, you can develop a comprehensive understanding of the literature related to your topic. This process includes evaluating research methods and critically analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of each source.
Ultimately, a well-structured literature review is integral to the research process. It demonstrates your ability to engage deeply with existing research, synthesize relevant sources, and provide a coherent analysis of the literature related to your research question.