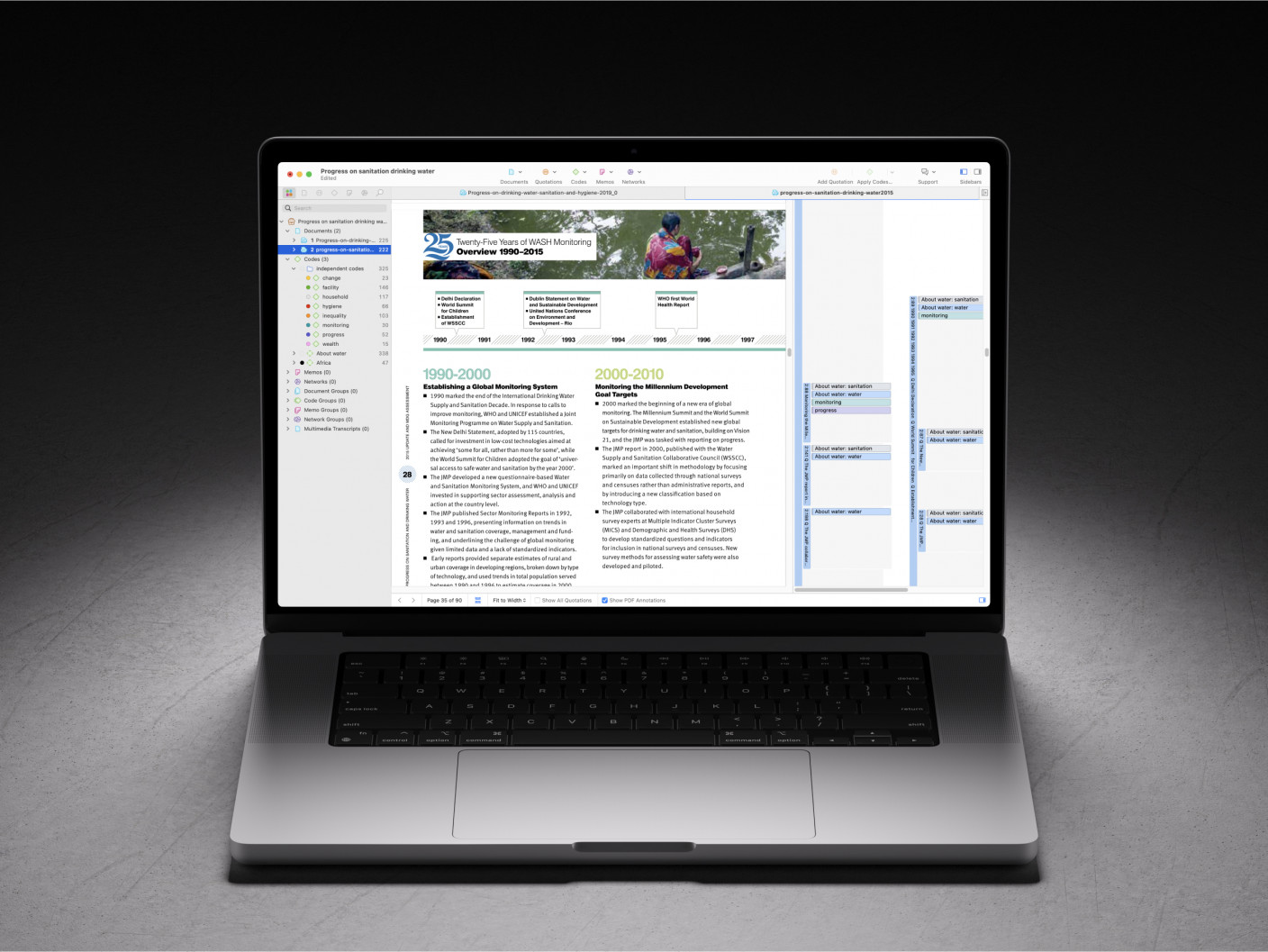
- What is a Literature Review?
- The Purpose of Literature Reviews
- Guidelines for Writing a Literature Review
- How to Organize a Literature Review?
- Software for Literature Reviews
- Using Artificial Intelligence for Literature Reviews
- How to Conduct a Literature Review?
- Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in a Literature Review
- Methods for Literature Reviews
- What is a Systematic Literature Review?
- What is a Narrative Literature Review?
- What is a Descriptive Literature Review?
- What is a Scoping Literature Review?
- What is a Realist Literature Review?
- What is a Critical Literature Review?
- Meta Analysis vs. Literature Review
- What is an Umbrella Literature Review?
- Differences Between Annotated Bibliographies and Literature Reviews
- Literature Review vs. Theoretical Framework
- How to Write a Literature Review?
- How to Structure a Literature Review?
- How to Make a Cover Page for a Literature Review?
- How to Write an Abstract for a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Introduction?
- How to Write the Body of a Literature Review?
- How to Write a Literature Review Conclusion?
- How to Make a Literature Review Bibliography?
- How to Format a Literature Review?
- How Long Should a Literature Review Be?
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- How to Present a Literature Review?
- How to Publish a Literature Review?
How to Make a Cover Page for a Literature Review?
A literature review cover page is the first point of contact between your research paper and your readers. It serves as a critical element that introduces your work and sets the tone for the entire document. A well-designed cover page provides essential details such as the paper title, author’s name, institutional affiliation and submission date. These elements help to contextualize your work within the academic or professional environment and ensure that your paper is properly identified and attributed.
Adhering to specific formatting guidelines, such as those outlined in the APA 7th edition guidelines, demonstrates your attention to detail and your commitment to maintaining high academic standards. In this article, we will explore the purpose and components of a literature review cover page, along with practical tips for creating an effective and professional-looking cover page. By following these guidelines, you can ensure that your literature review not only meets academic requirements but also makes a strong first impression on your readers.
What is included in the cover page of a literature review research paper?
The elements included in the cover page of a literature review can vary depending on the guidelines provided by your institution or the specific requirements of the publication. However, several key components are typically included:
Title of the literature review
The paper title should be centred and placed three to four lines down from the top margin of the page. It should be bold and written in the title case (capitalizing the first letter of major words). The title should be concise yet descriptive, clearly indicating the focus of your review.
Author’s name
Below the title, include your full name. If the review is a group effort, list all contributing authors. The names should be double-spaced and centred.
Institutional affiliation
Directly below the author’s name, include the name of your institution or organization. This helps contextualize your work within the academic or professional environment.
Date of submission
Finally, include the due date when the literature review is submitted. The date should be formatted appropriately (e.g., June 23, 2024) and placed below the author's institutional affiliation.
Formatting and writing tips
Creating a well-formatted and professional cover page requires attention to detail and adherence to specific formatting guidelines. Here are some tips based on APA format guidelines, though other formats exist and may be used depending on institutional requirements:
-
Use standard fonts and sizes: Use a standard font like Times New Roman in a 12-point size. This ensures readability and a professional appearance.
-
Double-space all text: Double-spacing makes the cover page easier to read and provides a clean layout. Each section should be separated by a double-spaced blank line.
-
Set 1-inch margins on all sides: Consistent margins are important for a neat and organized look.
-
Center all text on the cover page: Centering the text helps create a balanced and visually appealing page.
-
Follow specific guidelines: Always check for any specific formatting requirements provided by your institution or publication. This includes any instructions on the order and placement of information.
-
Include a running head and page number: For APA format, include a running head in the page header, aligned to the left, and a page number aligned to the right.
-
Be concise and clear: The title should be clear and concise, providing an accurate representation of your literature review's content. Avoid using jargon or overly complex language.
-
Consult the publication manual: Refer to the APA style guide or the specific publication manual for detailed instructions on formatting.
By following these guidelines based on APA 7th edition, you can create a well-formatted and professional cover page for your literature review. The cover page is the first thing your readers see, so it is important to make a good impression. A well-crafted cover page sets the stage for the rest of your work and demonstrates your attention to detail and adherence to academic standards.
References
American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). American Psychological Association.