- What is Interview Analysis?
- Advantages of Interviews in Research
- Disadvantages of Interviews in Research
- Ethical Considerations in Interviews
- Preparing a Research Interview
- Recruitment & Sampling for Research Interviews
- Interview Design
- How to Formulate Interview Questions
- Rapport in Interviews
- Social Desirability Bias
- Interviewer Effect
- Types of Research Interviews
- Face-to-Face Interviews
- Focus Group Interviews
- Email Interviews
- Telephone Interviews
- Stimulated Recall Interviews
- Interviews vs. Surveys
- Interviews vs Questionnaires
- Interviews and Interrogations
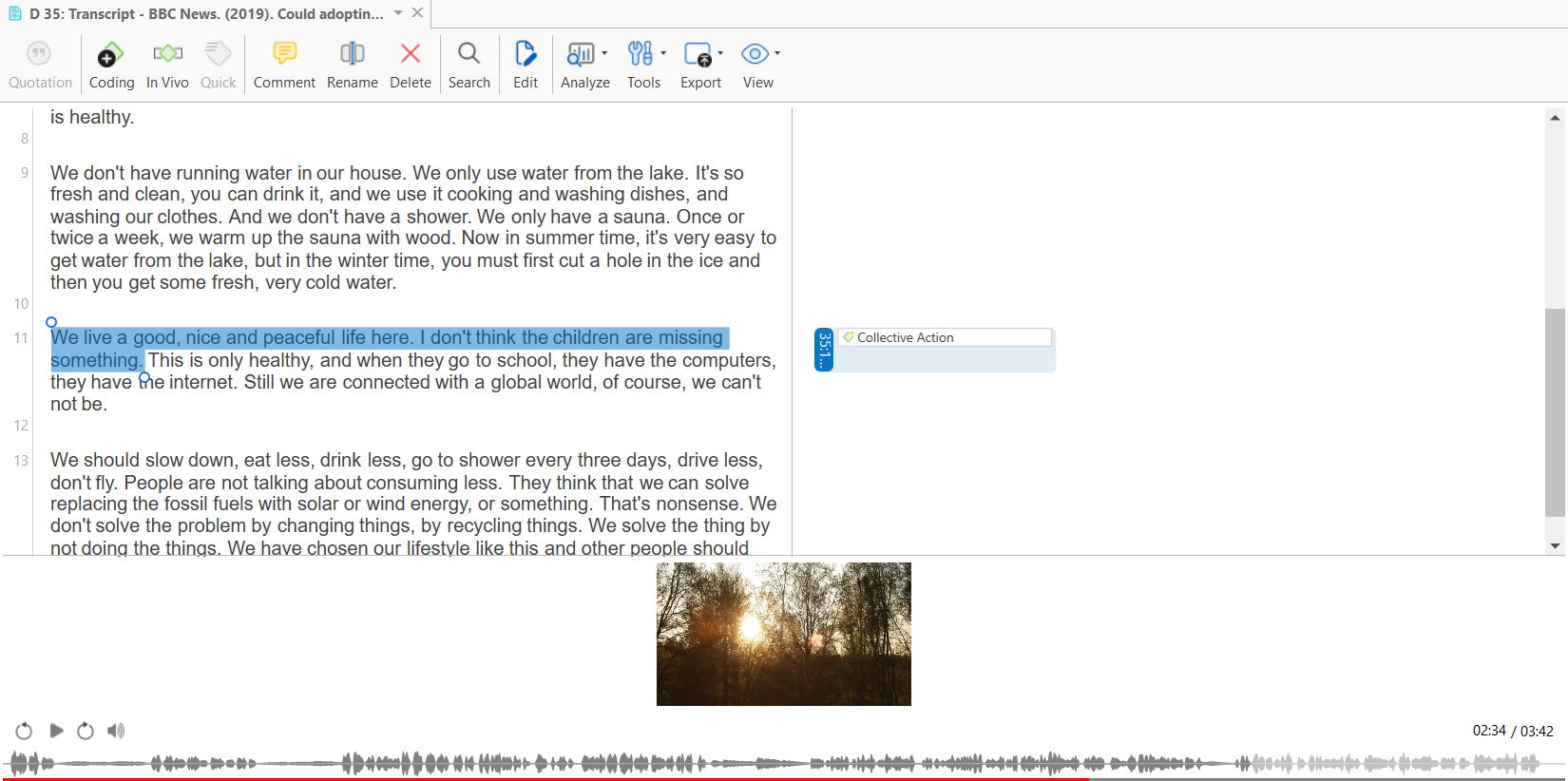
- How to Transcribe Interviews?
- Verbatim Transcription
- Clean Interview Transcriptions
- Manual Interview Transcription
- Automated Interview Transcription
- How to Annotate Research Interviews?
- Formatting and Anonymizing Interviews
- Analyzing Interviews
- Coding Interviews
- Reporting & Presenting Interview Findings
- How to cite "The Guide to Interview Analysis"
Automated Interview Transcription
Manual transcription can capture subtle conversational nuances and deliver a level of precision necessary for some research contexts. However, as projects become larger and deadlines more constrained, automated transcription has become an increasingly practical alternative, offering researchers a faster, scalable solution. Read this article to learn more about automated transcription, its benefits, disadvantages and some tools you can use for your audio or video files.

Introduction
While human transcription remains the gold standard for accurate transcription, advancements in technology have introduced a variety of transcription services that rely on AI-powered tools. Automated transcription services use advanced natural language processing to provide efficient handling of large volumes of data. The best transcription services can often process straightforward audio files in minutes, making them especially valuable when time and budget constraints limit the use of a traditional manual transcription. Transcription apps allow researchers to upload an audio recording and receive usable transcripts quickly, saving hours that would otherwise be spent on manual transcription or waiting for a human transcription service to transcribe an audio playback.
The choice between human and automated transcription depends on the audio file's complexity and the project’s goals. For example, audio recordings with multiple speakers, heavy accents, or nuanced expressions still benefit from the thoroughness that a human transcription service offers. Yet, as automated transcription continues to evolve, these tools are increasingly able to meet research needs, balancing speed and cost-effectiveness. With the ability to upload files directly, researchers can use automated transcription to process large datasets efficiently, allowing them to focus more on data analysis than transcription management.
When do researchers prefer automated transcription?
Automated transcription is often preferred when researchers need to process large datasets quickly. It’s especially useful for projects with tight deadlines or limited resources, as the transcription process is faster than manual methods. In situations where the research does not heavily rely on nuanced conversational elements, automated transcription can provide a sufficient level of accuracy.
For straightforward interviews, such as those with clear audio and a single speaker, automated systems are highly effective. They offer real-time transcription options and allow researchers to immediately begin their analysis without waiting for lengthy manual transcription processes. Automated transcription is also favored in cases where budget constraints limit the use of professional transcription services.
While the technology can struggle with complex audio, such as overlapping speech or strong accents, improvements in software mean that these systems continue to evolve and provide increasing levels of accuracy.
Benefits of automated transcription
Automated transcription offers several key advantages, particularly for researchers who need efficiency in their workflow. Here are some of the primary benefits:
Speed and efficiency
Automated transcription drastically reduces the time needed to convert audio into text. Researchers can upload an audio or video file, and the software will produce a written transcript in a fraction of the time it would take to transcribe manually. This allows researchers to focus more on data analysis and less on the labor-intensive transcription process.
Real-time transcription
Many automated transcription tools offer real-time transcription features, allowing researchers to capture spoken content immediately during interviews. This feature is particularly useful in live settings, such as focus groups or events, where having an instant transcript can be beneficial for immediate analysis or note-taking.
Cost-effective solution
Automated transcription can be a more affordable option compared to manual transcription services, especially for projects with limited budgets. Many transcription platforms offer pricing based on the number of minutes transcribed, making it easier to predict and control costs. For researchers dealing with high volumes of audio, automated transcription is a budget-friendly alternative to outsourcing.
Easily scalable
For large-scale projects involving dozens or even hundreds of interviews, automated transcription offers a scalable solution. Researchers can upload multiple files simultaneously and receive transcripts quickly, ensuring that the project remains on schedule without bottlenecks in the transcription process.
Simple integration with analysis tools
Many automated transcription platforms are designed to integrate with qualitative analysis tools such as ATLAS.ti or NVivo. This integration allows researchers to seamlessly import their transcripts into their analysis software for coding and further study, streamlining the overall research process.
Disadvantages of automated transcription
While automated transcription has its benefits, there are several limitations that researchers must be aware of when considering this method.
Accuracy limitations
Automated transcription systems can struggle with audio quality, accents, and overlapping speech, leading to errors in the final transcript. These errors can impact the quality of the analysis, especially in cases where precise wording is critical. For complex interviews, manual review and correction are often necessary to ensure that the transcript accurately reflects the conversation.
Loss of nuance
Automated systems cannot capture nonverbal cues like tone, pauses, or emotional expressions, which are often important in qualitative research. This lack of nuance can lead to a superficial transcript that misses key elements of the conversation. Researchers who rely on these subtleties may find automated transcription less useful.
Inconsistent results across languages
While some transcription software offers multilingual support, accuracy can vary widely depending on the language or dialect being used. Automated transcription tools are generally most accurate when working with widely spoken languages like English, but accuracy drops when dealing with less common languages or strong regional accents.
Manual review required
Even with advancements in automated transcription, a significant amount of manual review is often needed to correct mistakes. This review process can become time-consuming, especially when the original audio is complex or of poor quality, reducing the time-saving benefits of automation.

Tools and software for automated transcriptions
Automated transcription relies heavily on technology to convert speech into text quickly and efficiently. Here are some tools in the market that researchers can use for automated transcription:
Otter.ai
Advantages: Otter.ai offers real-time transcription, speaker identification, and integration with platforms like Zoom and Google Meet. It’s flexible for researchers conducting online interviews and provides editing tools for refining transcripts.
Disadvantages: Despite its convenience, Otter.ai can struggle with accuracy in noisy environments or with strong accents, requiring manual corrections. It also lacks advanced editing features that some other platforms offer.
Rev
Advantages: Rev provides both human and automated transcription services. Its human transcription option offers near-perfect accuracy, and the platform allows for easy editing within the same interface.
Disadvantages: The automated transcription is less accurate than the human service, especially with complex audio. The human transcription option is significantly more expensive, making it less ideal for large datasets.
Trint
Advantages: Trint is known for handling large audio files efficiently and offers strong collaborative editing tools. Its search and tagging features are beneficial for organizing and analyzing transcripts.
Disadvantages: Trint’s automated transcription, while accurate, can still miss details in poor-quality audio or with multiple speakers. Manual review and correction are often required, reducing the time-saving benefit.
Sonix
Advantages: Sonix provides automated transcription with strong editing tools, speaker labeling, and time-stamping. It integrates well with other platforms and can handle large volumes of data quickly.
Disadvantages: Sonix may struggle with highly technical language or strong accents, leading to errors. Additionally, its higher-tier features can make it a more costly option for budget-conscious researchers.
Temi
Advantages: Temi offers quick, budget-friendly transcription, making it ideal for researchers with simple audio files and limited resources.
Disadvantages: Temi is less accurate with complex audio or background noise and offers fewer advanced features for editing and collaboration. It’s best suited for straightforward transcription needs with clear audio.
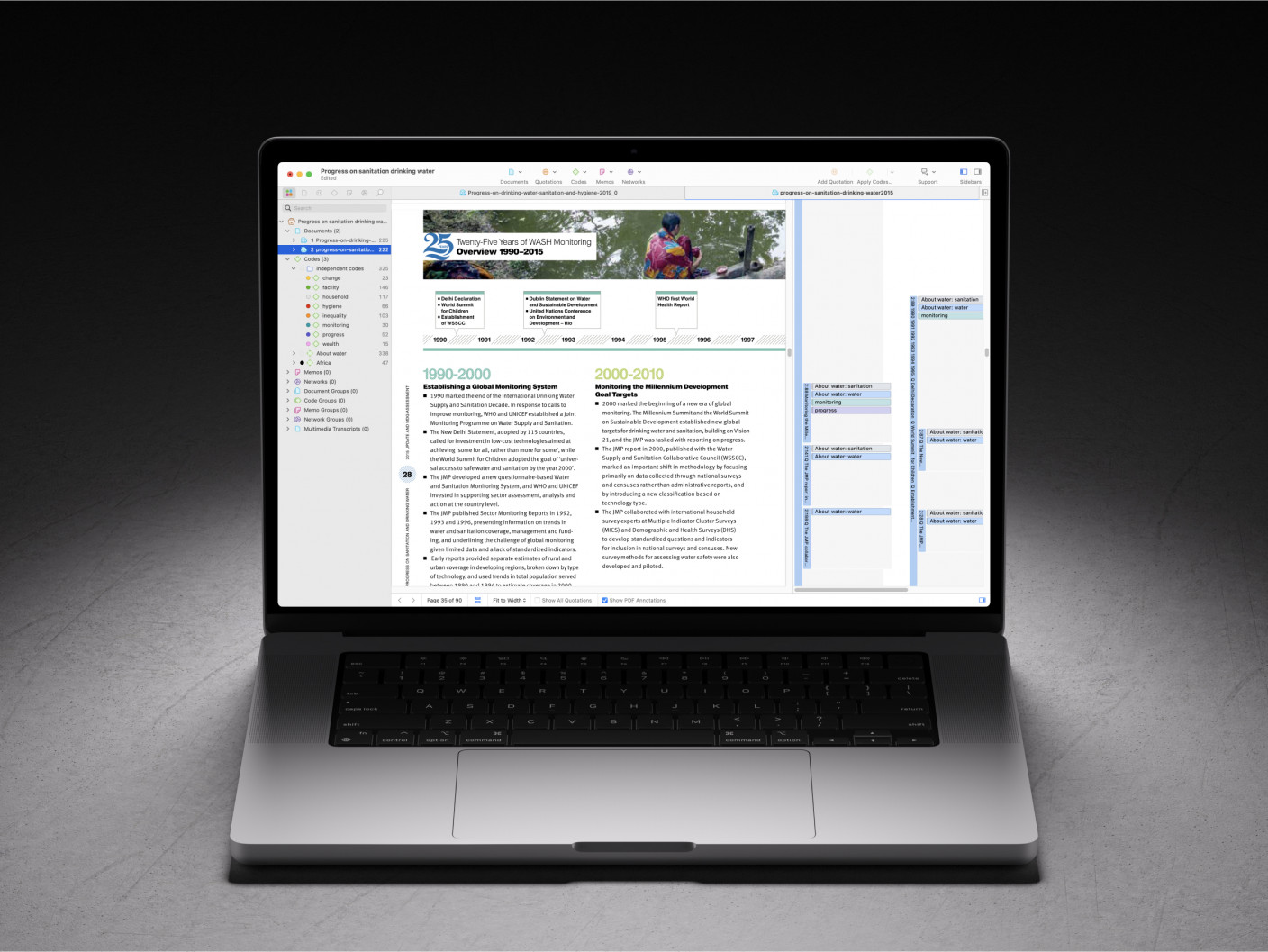
How can ATLAS.ti help you with automated transcripts?
ATLAS.ti provides distinct capabilities across ATLAS.ti Desktop and ATLAS.ti Web, both of which enhance the process of analyzing automated transcripts but cater to different research needs.
In ATLAS.ti Desktop, researchers have access to advanced AI-driven tools that greatly streamline transcript analysis. The AI-assisted coding feature automatically detects patterns and themes within the text, allowing researchers to quickly apply relevant codes across large datasets. This is especially valuable when handling extensive transcripts, as the AI helps to reduce manual work while maintaining high analytical precision.
Additionally, AI-powered sentiment analysis in ATLAS.ti Desktop offers deep insights into the emotional tone of the transcripts, helping researchers understand the underlying sentiments expressed by participants. With the Query Tool and Code-Document Table, ATLAS.ti Desktop enables in-depth exploration of coded data, making it easy to track relationships between codes and identify significant patterns or trends within the transcripts. These tools provide researchers with a powerful framework for organizing, categorizing, and drawing conclusions from their coded data.
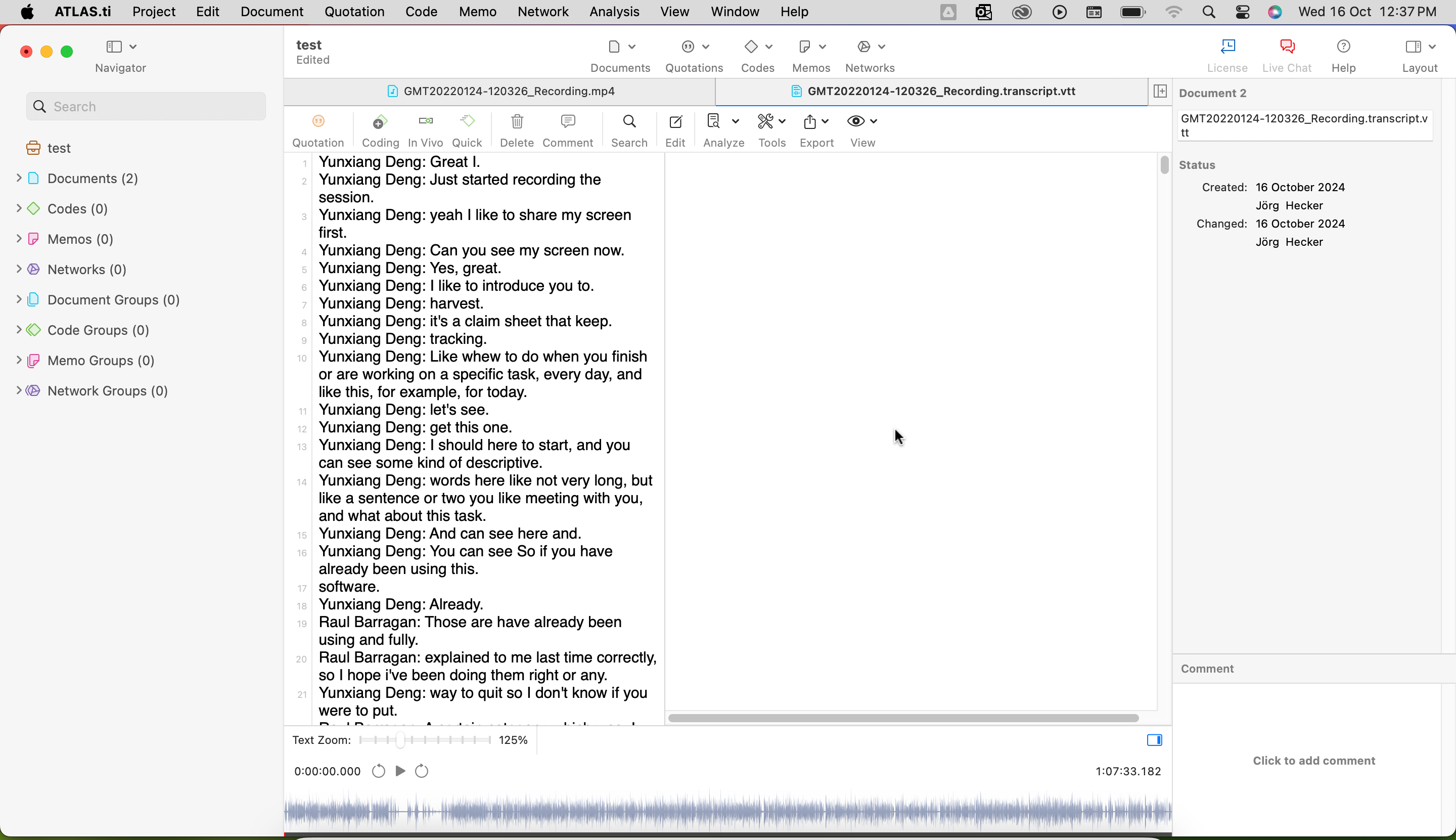
ATLAS.ti Web is designed for flexible, real-time collaboration on transcript analysis, making it ideal for research teams. Researchers can work together from different locations, sharing projects and analyzing transcripts simultaneously. In ATLAS.ti Web, users can easily create quotations to mark relevant sections of the transcript and apply codes to organize the data. This helps to structure the analysis by segmenting important portions of the text for deeper exploration. The platform is intuitive, offering a browser-based environment that supports collaborative coding and project management, all in real time. It ensures that teams can work together efficiently on projects without needing to download or install additional software.
Both ATLAS.ti Desktop and ATLAS.ti Web offer seamless integration of automated transcripts, allowing researchers to focus on analyzing the content rather than managing files. All versions of ATLAS.ti are perfect for those needing advanced AI features and deep analytic capabilities, while ATLAS.ti Web offers a streamlined, collaborative environment for working on transcripts with colleagues in a live setting.
Conclusion
Automated transcription has become an essential tool for qualitative researchers, providing fast, scalable, and cost-effective solutions to convert spoken content into text. While human transcription still offers the highest accuracy, especially for complex audio or nuanced conversations, AI-driven transcription services have made significant strides in efficiency and reliability. These tools are particularly valuable for large-scale projects or when time and budget constraints are a concern, offering features like real-time transcription, speaker identification, and seamless integration with qualitative analysis platforms.
As technology continues to evolve, automated transcription will likely play an even larger role in qualitative research, helping researchers handle increasing amounts of data with speed and precision. Platforms like ATLAS.ti complement these services by offering robust analysis tools, ensuring that researchers can easily organize, code, and draw insights from their transcribed data, further enhancing the research process.