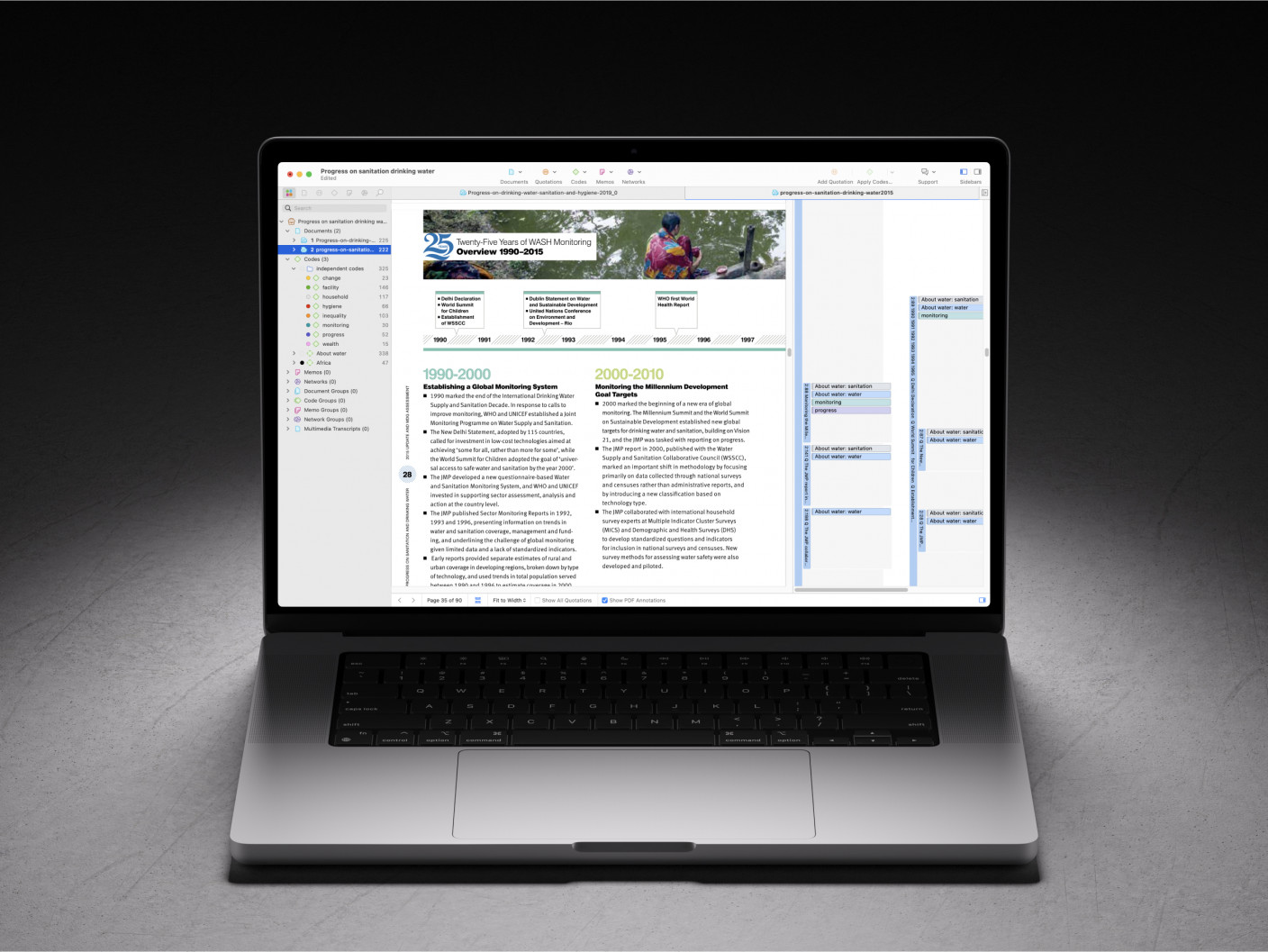
- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Interviews
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Surveys
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Bias
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
- How to cite "The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics"
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is an essential approach in various academic disciplines and professional fields, as it seeks to understand and interpret the meanings, experiences, and social realities of people in their natural settings. This type of research employs an array of qualitative methods to gather and analyze non-numerical data, such as words, images, and behaviors, and aims to generate in-depth and contextualized insights into the phenomena under study.

Basics of qualitative research
Qualitative research is designed to address research questions that focus on understanding the "why" and "how" of human behavior, experiences, and interactions, rather than just the "what" or "how many" that quantitative methods typically seek to answer. The main purpose of qualitative research is to gain a rich and nuanced understanding of people's perspectives, emotions, beliefs, and motivations in relation to specific issues, situations, or phenomena.
Characteristics of qualitative research
Several key characteristics distinguish qualitative research from other types of research, such as quantitative research:
-
Naturalistic settings: Qualitative researchers collect data in the real-world settings where the phenomena of interest occur, rather than in controlled laboratory environments. This allows researchers to observe and understand the participants' behavior, experiences, and social interactions in their natural context.
-
Inductive approach: Unlike quantitative research, which often follows a deductive approach, qualitative research begins with the collection of data and then seeks to develop theories, concepts, or themes that emerge from the data. This inductive approach enables researchers to stay open to new insights and unexpected findings.
-
Holistic perspective: Qualitative research aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the phenomena under study by considering multiple dimensions, such as the social, cultural, historical, and psychological aspects that shape people's experiences and behavior.
-
Subjectivity and interpretation: Epistemology plays a key role in qualitative research. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their biases, assumptions, and values, and to consider how these may influence their data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
-
Flexibility: Qualitative research methods are often flexible and adaptable, allowing researchers to refine their research questions, sampling strategies, or data collection techniques as new insights and perspectives emerge during the research process.
Key principles of qualitative research
Qualitative research is guided by several fundamental principles that shape its approach, methods, and analysis:
-
Empathy and reflexivity: Qualitative researchers strive to empathize with the participants and to understand their perspectives, experiences, and emotions from their viewpoint. This requires researchers to be attentive, open-minded, and sensitive to the participants' verbal and non-verbal cues. At the same, qualitative researchers critically reflect on their participants’ perspectives, experiences, and emotions to develop their findings and conclusions, instead of taking these at face value. In addition, it is important for the researcher to reflect on how their own role and viewpoint may be shaping the research.
-
Trustworthiness: Establishing trustworthiness in qualitative research involves demonstrating credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability. Researchers can enhance trustworthiness by using various strategies, such as triangulation, member checking, peer debriefing, and reflexivity.
-
Iterative analysis: Qualitative data analysis is an ongoing and iterative process, in which researchers continually review, compare, and revise their interpretations as they collect and analyze more data. This iterative process allows researchers to refine their understanding of the phenomena and to develop more robust and nuanced theories, concepts, or themes.
-
Rich description: Providing detailed, vivid, and context-sensitive descriptions of the data is essential in qualitative research. Rich descriptions help convey the complexity and nuances of the phenomena under study, and enable readers to assess the relevance and transferability of the findings to other settings or populations.

Types, aspects, examples
What are the common types of qualitative research?
Qualitative research is an umbrella term for various methodologies that focus on understanding and interpreting human experiences, behaviors, and social phenomena within their context. These approaches seek to gather in-depth, rich data through the analysis of language, actions, and expressions. Five common types of qualitative research are narrative research, phenomenology, grounded theory, ethnography, and case study.
-
Narrative research: This approach focuses on the stories and experiences of individuals, aiming to understand their lives and personal perspectives. Researchers can collect data through interviews, letters, diaries, or autobiographies, and analyze these narratives to identify recurring themes, patterns, and meanings. Narrative research can be valuable for exploring individual identities, cultural beliefs, and historical events.
-
Phenomenology: Phenomenology seeks to understand the essence of a particular phenomenon by analyzing the experiences and perceptions of individuals who have gone through that phenomenon . Researchers can explore participants' thoughts, feelings, and experiences through in-depth interviews, observations, or written materials. The goal is to describe the commonalities and variations in these experiences, ultimately revealing the underlying structures and meaning of the phenomenon under study.
-
Grounded theory: This inductive research method aims to generate new theories by systematically collecting and analyzing data. Researchers begin with an open-ended research question and gather data through observations, interviews, and document analysis. They then use a process of coding and constant comparison to identify patterns, categories, and relationships in the data. This iterative process continues until a comprehensive, grounded theory emerges that is based in the recollected data and explains the topic of interest.
-
Ethnography: Ethnographic research involves the in-depth study of a specific cultural or social group, focusing on understanding its members' behaviors, beliefs, and interactions. Researchers immerse themselves in the group's environment, often for extended periods, to observe and participate in daily activities. They can collect data through field notes, interviews, and document analysis, aiming to provide a holistic and nuanced understanding of the group's cultural practices and social dynamics.
-
Case study: A case study is an in-depth examination of a specific instance, event, organization, or individual within its real-life context. Researchers use multiple sources of data, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts to build a rich, detailed understanding of the case. Case study research can be used to explore complex phenomena, generate new hypotheses, or evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or policies.
What are the purposes of qualitative research?
Qualitative research presents outcomes that emerge from the process of collecting and analyzing qualitative data. These outcomes often involve generating new theories, developing or challenging existing theories, and proposing practical implications based on actionable insights. The products of qualitative research contribute to a deeper understanding of human experiences, social phenomena, and cultural contexts. Qualitative research can also be a powerful complement to quantitative research.
-
Generating new theory: One of the primary goals of qualitative research is to develop new theories or conceptual frameworks that help explain previously unexplored or poorly understood phenomena. By conducting in-depth investigations and analyzing rich data, researchers can identify patterns, relationships, and underlying structures that form the basis of novel theoretical insights.
-
Developing or challenging existing theory: Qualitative research can also contribute to the refinement or expansion of existing theories by providing new perspectives, revealing previously unnoticed complexities, or highlighting areas where current theories may be insufficient or inaccurate. By examining the nuances and context-specific details of a phenomenon, researchers can generate evidence that supports, contradicts, or modifies existing theoretical frameworks.
-
Proposing practical implications: Qualitative research often yields actionable insights that can inform policy, practice, and intervention strategies. By exploring the lived experiences of individuals and communities, researchers can identify factors that contribute to or hinder the effectiveness of certain approaches, uncovering opportunities for improvement or innovation. The insights gained from qualitative research can be used to design targeted interventions, develop context-sensitive policies, or inform the professional practices of practitioners in various fields.
-
Enhancing understanding and empathy: Qualitative research promotes a deeper understanding of human experiences, emotions, and perspectives, fostering empathy and cultural sensitivity. By engaging with diverse voices and experiences, researchers can develop a more nuanced appreciation of the complexities of human behavior and social dynamics, ultimately contributing to more compassionate and inclusive societies.
-
Informing mixed-methods research: The products of qualitative research can also be used in conjunction with quantitative research, as part of a mixed-methods approach. Qualitative findings can help generate hypotheses for further testing, inform the development of survey instruments, or provide context and explanation for quantitative results. Combining the strengths of both approaches can lead to more robust and comprehensive understanding of complex research questions.
What are some examples of qualitative research?
Qualitative research can be conducted across various scientific fields, exploring diverse topics and phenomena. Here are six brief descriptions of qualitative studies that can provide researchers with ideas for their own projects:
-
Exploring the lived experiences of refugees: A phenomenological study could be conducted to investigate the lived experiences and coping strategies of refugees in a specific host country. By conducting in-depth interviews with refugees and analyzing their narratives, researchers can gain insights into the challenges they face, their resilience, and the factors that contribute to successful integration into their new communities.
-
Understanding the dynamics of online communities: An ethnographic study could be designed to explore the culture and social dynamics of a particular online community or social media platform. By immersing themselves in the virtual environment, researchers can observe patterns of interaction, communication styles, and shared values among community members, providing a nuanced understanding of the factors that influence online behavior and group dynamics.
-
Examining the impact of gentrification on local communities: A case study could be conducted to explore the impact of gentrification on a specific neighborhood or community. Researchers can collect data through interviews with residents, local business owners, and policymakers, as well as analyzing relevant documents and media coverage. The study can shed light on the effects of gentrification on housing affordability, social cohesion, and cultural identity, informing policy and urban planning decisions.
-
Studying the career trajectories of women in STEM fields: A narrative research project can be designed to investigate the career experiences and pathways of women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields. By collecting and analyzing the stories of women at various career stages, researchers can identify factors that contribute to their success, as well as barriers and challenges they face in male-dominated fields.
-
Evaluating the effectiveness of a mental health intervention: A qualitative study can be conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of a specific mental health intervention, such as a mindfulness-based program for reducing stress and anxiety. Researchers can gather data through interviews and focus groups with program participants, exploring their experiences, perceived benefits, and suggestions for improvement. The findings can provide valuable insights for refining the intervention and informing future mental health initiatives.
-
Investigating the role of social media in political activism: A qualitative study using document analysis and visual methods could explore the role of social media in shaping political activism and public opinion during a specific social movement or election campaign. By analyzing user-generated content, such as tweets, posts, images, and videos, researchers can examine patterns of communication, mobilization, and discourse, shedding light on the ways in which social media influences political engagement and democratic processes.
What are common qualitative research methods?
Qualitative research methods are techniques used to collect, analyze, and interpret data in qualitative studies. These methods prioritize the exploration of meaning, context, and individual experiences. Common qualitative research methods include interviews, focus groups, observations, document analysis, and visual methods.
-
Interviews: Interviews involve one-on-one conversations between the researcher and the participant. They can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured, depending on the level of guidance provided by the researcher. Interviews allow for in-depth exploration of participants' experiences, thoughts, and feelings, providing rich and detailed data for analysis.
-
Focus groups: Focus groups are group discussions facilitated by a researcher, usually consisting of 6-12 participants. They enable researchers to explore participants' collective perspectives, opinions, and experiences in a social setting. Focus groups can generate insights into group dynamics, cultural norms, and shared understandings, as participants interact and respond to each other's viewpoints.
-
Observations: Observational research involves the systematic collection of data through watching and recording people, events, or behaviors in their natural settings. Researchers can take on different roles, such as participant-observer or non-participant observer, depending on their level of involvement. Observations provide valuable information about context, social interactions, and non-verbal communication, which can help researchers understand the nuances of a particular phenomenon.
-
Document analysis: Document analysis is the examination of written or visual materials, such as letters, diaries, reports, newspaper articles, photographs, or videos. This method can provide insights into historical or cultural contexts, individual perspectives, and organizational processes. Researchers may use content analysis, discourse analysis, or other analytic techniques to interpret the meaning and significance of these documents.
-
Visual methods: Visual methods involve the use of visual materials, such as photographs, drawings, or videos, to explore and represent participants' experiences and perspectives. Techniques like photo elicitation, where participants are asked to take or select photographs related to the research topic and discuss their meaning, can encourage reflection and stimulate discussion. Visual methods can be particularly useful in capturing non-verbal information, promoting cross-cultural understanding, and engaging with hard-to-reach populations.

Benefits and challenges
Importance of qualitative research and qualitative data analysis
Qualitative research and qualitative data analysis play a major role in advancing knowledge, informing policies, and improving practices in various fields, such as education, healthcare, business, and social work. The unique insights and in-depth understanding generated through qualitative research can accomplish a number of goals.
Inform decision-making
Qualitative research helps decision-makers better understand the needs, preferences, and concerns of different stakeholders, such as customers, employees, or community members. This can lead to more effective and tailored policies, programs, or interventions that address real-world challenges.
Enhance innovation
By exploring people's experiences, motivations, and aspirations, qualitative research can uncover new ideas, opportunities, and trends that can drive innovation in products, services, or processes.
Foster empathy and cultural competence
Qualitative research can increase our empathy and understanding of diverse populations, cultures, and contexts. This can enhance our ability to communicate, collaborate, and work effectively with people from different backgrounds.
Complement quantitative research
Qualitative research can complement quantitative research by providing rich contextual information and in-depth insights into the underlying mechanisms, processes, or factors that may explain the patterns or relationships observed in quantitative data.
Facilitate social change
Qualitative research can give voice to marginalized or underrepresented groups, highlight social injustices or inequalities, and inspire actions and reforms that promote social change and well-being.
Challenges of conducting qualitative research
While qualitative research offers valuable insights and understanding of human experiences, it also presents some challenges that researchers must navigate. Acknowledging and addressing these challenges can help ensure the rigor, credibility, and relevance of qualitative research. In this section, we will discuss some common challenges that researchers may encounter when conducting qualitative research and offer suggestions on how to overcome them.
Subjectivity and bias
One of the primary challenges in qualitative research is managing subjectivity and potential biases that may arise from the researcher's personal beliefs, values, and experiences. Since qualitative research relies on the researcher's interpretation of the data, there is a risk that the researcher's subjectivity may influence the findings.
Researchers can minimize the impact of subjectivity and bias by maintaining reflexivity, or ongoing self-awareness and critical reflection on their role, assumptions, and influences in the research process. This may involve keeping a reflexive journal, engaging in peer debriefing, and discussing potential biases with research participants during member checking.
Data collection and quality
Collecting high-quality data in qualitative research can be challenging, particularly when dealing with sensitive topics, hard-to-reach populations, or complex social phenomena. Ensuring the trustworthiness of qualitative data collection is essential to producing credible and meaningful findings.
Researchers can enhance data quality by employing various strategies, such as purposive or theoretical sampling, triangulation of data sources, methods or researchers, and establishing rapport and trust with research participants.
Data analysis and interpretation
The analysis and interpretation of qualitative data can be a complex, time-consuming, and sometimes overwhelming process. Researchers must make sense of large amounts of diverse and unstructured data, while also ensuring the rigor, transparency, and consistency of their analysis.
Researchers can facilitate data analysis and interpretation by adopting systematic and well-established approaches, such as thematic analysis, grounded theory, or content analysis. Utilizing qualitative data analysis software, like ATLAS.ti, can also help manage and analyze data more efficiently and rigorously.
Ethical considerations
Qualitative research often involves exploring sensitive issues or working with vulnerable populations, which raises various ethical considerations, such as privacy, confidentiality, informed consent, and potential harm to participants.
Researchers should be familiar with the ethical guidelines and requirements of their discipline, institution, or funding agency, and should obtain ethical approval from relevant review boards or committees before conducting the research. Researchers should also maintain open communication with participants, respect their autonomy and dignity, and protect their well-being throughout the research process.
Generalizability and transferability
Qualitative research typically focuses on in-depth exploration of specific cases or contexts, which may limit the generalizability or transferability of the findings to other settings or populations. However, the goal of qualitative research is not to produce statistically generalizable results but rather to provide a rich, contextualized, and nuanced understanding of the phenomena under study.
Researchers can enhance the transferability of their findings by providing rich descriptions of the research context, participants, and methods, and by discussing the potential applicability or relevance of the findings to other settings or populations. Readers can then assess the transferability of the findings based on the similarity of their own context to the one described in the research.
By addressing these challenges and adopting rigorous and transparent research practices, qualitative researchers can contribute valuable and meaningful insights that advance knowledge, inform policies, and improve practices in various fields and contexts.
How qualitative research complements quantitative research
Qualitative and quantitative research approaches are often seen as distinct and even opposing paradigms. However, these two approaches can be complementary, providing a more comprehensive understanding of complex social phenomena when combined. In this section, we will discuss how qualitative research can complement quantitative research and enhance the overall depth, breadth, and rigor of research findings.
Exploring and understanding context
Quantitative research identifies patterns, trends, and relationships among variables using numerical data, while qualitative research provides rich and nuanced insights into the context, meaning, and underlying processes that shape these patterns or relationships. By integrating qualitative research with quantitative research, researchers can explore not only the "what" or "how many" but also the "why" and "how" of the phenomena under study.
For example, a quantitative study in health services research might reveal a correlation between social media usage and mental health outcomes, while a qualitative study could help explain the reasons behind this correlation by exploring users' experiences, motivations, and perceptions of social media. Qualitative and quantitative data in this case complement each other to contribute to a more robust theory and more informed policy implications.
Generating and refining hypotheses
Qualitative research can inform the development and refinement of hypotheses for quantitative research by identifying new concepts, variables, or relationships that emerge from the data. This can lead to more focused, relevant, and innovative quantitative research questions and hypotheses.
For instance, a qualitative study on employee motivation might uncover the importance of meaningful work and supportive relationships with supervisors as key factors influencing motivation. These findings could then be incorporated into a quantitative study to test the relationships between these factors and employee motivation.
Validating and triangulating findings
Combining qualitative and quantitative research methods can enhance the credibility and trustworthiness of research findings through validation and triangulation. Validation involves comparing the findings from different methods to assess their consistency and convergence, while triangulation involves using multiple methods, data sources, or researchers to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomena under study.
For example, a researcher might use both quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews in a mixed methods research design to assess the effectiveness of a health intervention. If both methods yield similar findings, this can increase confidence in the results. If the findings differ, the researcher can further investigate the reasons for these discrepancies and refine their understanding of the intervention's effectiveness.
Enhancing communication and dissemination
Qualitative research can enhance the communication and dissemination of quantitative research findings by providing vivid narratives, case studies, or examples that bring the data to life and make it more accessible and engaging for diverse audiences, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the public.
For example, a quantitative study on the impact of a community-based program might report the percentage of participants who experienced improvements in various outcomes. By adding qualitative data, such as quotes or stories from participants, the researcher can illustrate the human impact of the program and make the findings more compelling and relatable.
In conclusion, qualitative research can complement and enrich quantitative research in various ways, leading to a more comprehensive, contextualized, and rigorous understanding of complex social phenomena. By integrating qualitative and quantitative research methods, researchers can harness the strengths of both approaches to produce more robust, relevant, and impactful findings that inform theory, policy, and practice.
How is qualitative research reported?
Qualitative research findings are typically reported in various formats, depending on the audience, purpose, and context of the research. Common ways to report qualitative research include dissertations, journal articles, market research reports, and needs assessment reports. Each format has its own structure and emphasis, tailored to meet the expectations and requirements of its target audience.

-
Dissertations and theses: Doctoral,master's, or bachelor students often conduct qualitative research as part of their dissertation or thesis projects. In this format, researchers provide a comprehensive account of their research questions, methodology, data collection, data analysis, and findings. Dissertations are expected to make a significant contribution to the existing body of knowledge and demonstrate the researcher's mastery of the subject matter.
-
Journal articles: Researchers frequently disseminate their qualitative research findings through articles published in academic journals. These articles are typically structured in a way that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and discussion sections. In addition, articles often undergo a peer-review process before being published in the academic journal. Journal articles focus on communicating the study's purpose, methods, and findings in a concise and coherent manner, providing enough detail for other researchers to evaluate the rigor and validity of the research so that they can cite the article and build on it in their own studies.
-
Market research reports: Market research often employs qualitative methods to gather insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and attitudes. Market research reports present the findings of these studies to clients, typically businesses or organizations interested in understanding their target audience or market trends. These reports focus on providing actionable insights and recommendations based on the qualitative data, helping clients make informed decisions and develop effective marketing strategies.
-
Needs assessment reports: Needs assessment is a process used to identify gaps or areas of improvement in a specific context, such as healthcare, education, or social services. Qualitative research methods can be used to collect data on the needs, challenges, and experiences of the target population. Needs assessment reports present the findings of this research, highlighting the identified needs and providing recommendations for addressing them. These reports are used by organizations and policymakers to inform the development and implementation of targeted interventions and policies.
-
Other formats: In addition to the aforementioned formats, qualitative research findings can also be reported in conference presentations, white papers, policy briefs, blog posts, or multimedia presentations. The choice of format depends on the target audience and the intended purpose of the research, as well as the researcher's preferences and resources. Regardless of the format, it is important for researchers to present their findings in a clear, accurate, and engaging manner, ensuring that their work is accessible and relevant to their audience.