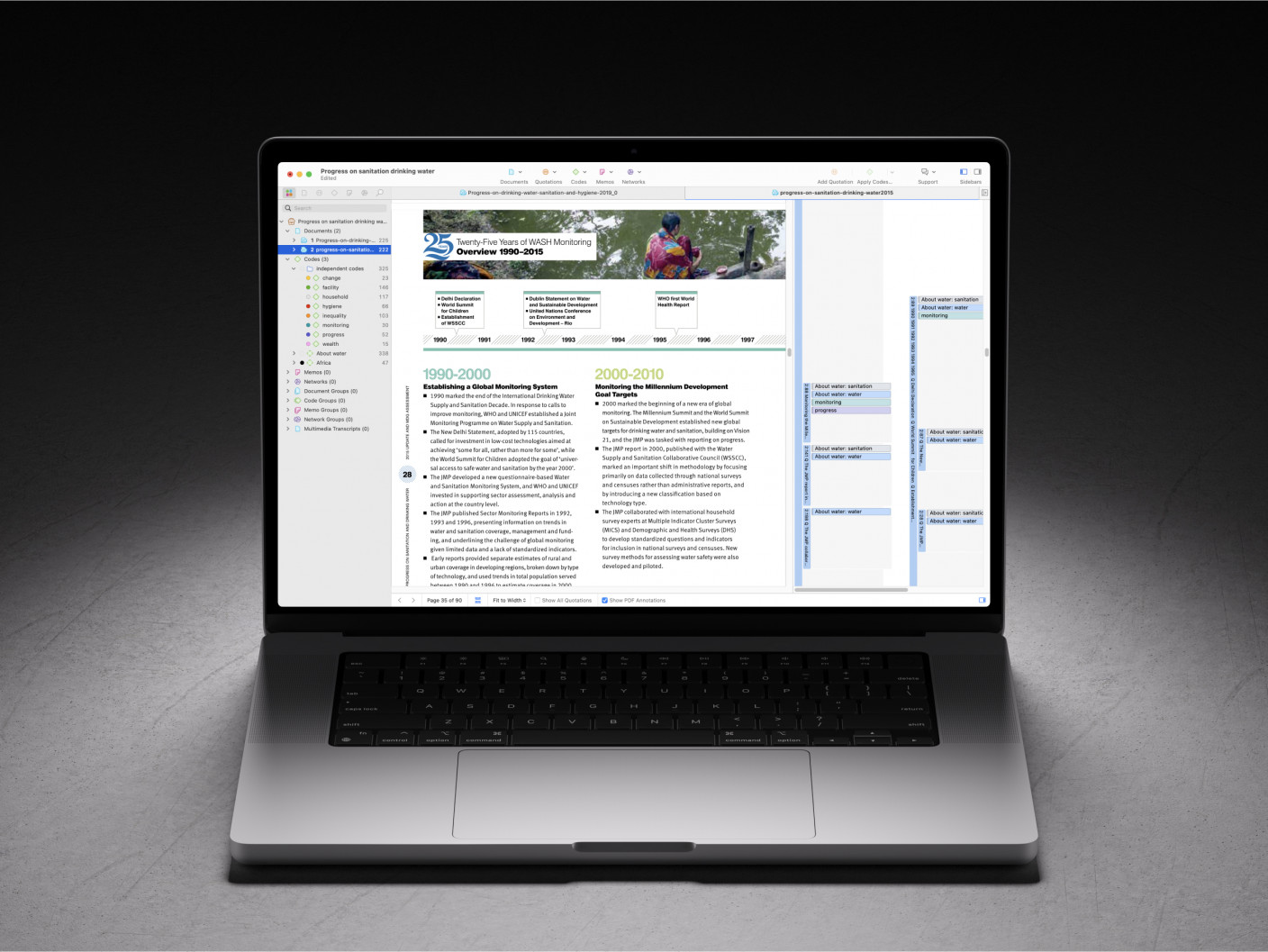
- What is Thematic Analysis?
- Advantages of Thematic Analysis
- Disadvantages of Thematic Analysis
- Thematic Analysis Examples
- How to Do Thematic Analysis
- Thematic Coding
- Collaborative Thematic Analysis
- Thematic Analysis Software
- Thematic Analysis in Mixed Methods Approach
- Abductive Thematic Analysis
- Deductive Thematic Analysis
- Inductive Thematic Analysis
- Reflexive Thematic Analysis
- Thematic Analysis in Observations
- Thematic Analysis in Surveys
- Thematic Analysis for Interviews
- Thematic Analysis for Focus Groups
- Thematic Analysis for Case Studies
- Thematic Analysis of Secondary Data
- Thematic Analysis Literature Review
- Thematic Analysis vs. Phenomenology
- Thematic vs. Content Analysis
- Thematic Analysis vs. Grounded Theory
- Thematic Analysis vs. Narrative Analysis
- Thematic Analysis vs. Discourse Analysis
- Thematic Analysis vs. Framework Analysis
- Thematic Analysis in Social Work
- Thematic Analysis in Psychology
- Thematic Analysis in Educational Research
- Thematic Analysis in UX Research
- How to Present Thematic Analysis Results
- Increasing Rigor in Thematic Analysis
- Peer Review in Thematic Analysis
- How to cite "The Guide to Thematic Analysis"
Thematic Analysis in UX Research
In this article, we focus on the application of thematic analysis within the context of user experience (UX) research. Thematic analysis is a systematic method used to identify themes within data. It provides an accessible and flexible approach for analyzing qualitative data, making it a valuable method for UX researchers looking to uncover insights into user behavior, preferences, and experiences.
This article outlines the basics of UX research, introduces thematic analysis as it pertains to UX research, discusses when it's appropriate to use thematic analysis, describes the process, and highlights challenges that may arise when analyzing user research data. Our goal is to present a clear and concise overview that assists qualitative researchers in understanding how thematic analysis can be effectively applied to a user research project.
What is UX research?
User experience (UX) research focuses on understanding user behaviors, needs, and motivations through observation techniques, task analysis, and other feedback methodologies. It is a critical component of UX design, aimed at enhancing the usability, accessibility, and pleasure provided in the interaction between the user and the product.
UX research encompasses a range of methods and tools, from interviews and surveys to usability testing and analytics. The core objective is to gather insights that inform design decisions and improve user satisfaction.
UX research can be divided into two main types: quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns and measure user behavior. It can answer the "how" of user behavior, providing metrics that can assess usability and effectiveness.
Qualitative research, on the other hand, tends to focus on understanding the "why" behind user actions and attitudes. It involves collecting non-numerical data, such as user opinions and feelings, through qualitative research methods like interviews, focus groups, and observational studies.
Effective UX research combines both quantitative and qualitative data, offering a comprehensive view of user experience. By identifying user needs and problems, UX research guides the design process towards solutions that are both meaningful and valuable to the user.
This, in turn, contributes to the creation of products that are not only functional but also resonate on a deeper level with their intended audience.
Types of data in UX research
User experience (UX) research generates a wealth of data, both quantitative and qualitative, each providing distinct insights into user interactions, behaviors, and attitudes.
Quantitative data, derived from methods like surveys, analytics, and usability tests, offers numerical insights that can highlight patterns, frequencies, and statistical relationships.
This type of data is essential for measuring user behavior at scale, assessing the usability of a product, and identifying areas for improvement based on objective metrics.
Qualitative data, on the other hand, can come from interviews, open-ended survey responses, observations, and diary studies. It dives deeper into the "why" behind user actions, preferences, and feelings, offering a rich, contextual understanding of the user experience.
While quantitative data tells us what is happening, qualitative data provides the nuances and stories behind those numbers, giving depth to user feedback and uncovering the motivations, challenges, and needs of users.
Both types of data play crucial roles in UX research, but our focus shifts towards qualitative data as we prepare to delve into thematic analysis. Thematic analysis serves as a powerful method to systematically interpret and make sense of the vast, nuanced information that qualitative data holds, ultimately guiding design improvements and strategic decisions.
By setting the stage with both quantitative and qualitative data types, we lay the groundwork for a deeper exploration of how thematic analysis can unravel the complexities of user experience, providing actionable insights and a more comprehensive understanding of user needs.
Analyzing qualitative data from UX research
Analyzing qualitative data from UX research involves a detailed examination of non-numerical data, such as user interviews, observations, and open-ended survey responses. This process is aimed at uncovering patterns, themes, and insights that can inform design decisions and enhance user satisfaction.
Unlike quantitative analysis, which relies on statistical methods to interpret data, qualitative analysis requires a nuanced approach, emphasizing iterative interpretation and understanding of user perspectives, experiences, and behaviors.
Researchers analyze qualitative data with a careful and systematic review of the material. Researchers look for recurring patterns, notable anomalies, and deep insights into the user experience. This may involve coding the data, or tagging parts of the data with labels that summarize the essence of what has been said or observed. These codes are then grouped into themes that reflect broader insights about the user experience.
A key aspect of qualitative data analysis in UX research is the iterative nature of the process. It is common for researchers to cycle back to the data multiple times, refining their codes and themes as their understanding deepens. This iterative process helps to ensure that the analysis remains grounded in the data while also being responsive to new insights that emerge.
Furthermore, analyzing qualitative data demands a balance between describing the data and interpreting it within the context of the broader user experience and research objectives. Researchers must remain open to the data's complexities and nuances, allowing the voices of users to guide the analysis and the resulting insights.
This qualitative analysis lays the foundation for thematic analysis, an analysis method that focuses on identifying and interpreting patterns of meaning across the data set. As we proceed, the emphasis will be on how thematic analysis specifically can be employed to draw out significant themes that provide a deep understanding of user experiences, guiding UX design and strategy.

What is thematic analysis for UX research?
Thematic analysis for UX research is an approach to qualitative analysis methods that systematically identifies, organizes, and offers insight into patterns of meaning (themes) across a dataset. These themes are crucial in capturing and interpreting the complexities of the user experience, providing a structured approach to understanding users' behaviors, preferences, and challenges.
In the context of UX research, a robust thematic analysis method transforms raw data—such as interview transcripts, field notes, and open-ended survey responses—into a coherent, insightful narrative about the user experience.
Conducting thematic analysis involves several key stages: familiarizing oneself with all the data, generating initial codes, searching for themes, reviewing themes, defining and naming themes, and finally, producing the report.
Initially, researchers immerse themselves in the data to gain an in-depth understanding. This immersion is crucial for recognizing subtle patterns and nuances. Subsequently, data is systematically coded, which involves tagging data segments with labels that summarize their essential qualities. These codes are then examined for patterns that suggest broader themes, capturing something important about the data in relation to your research questions.
Thematic analysis stands out for its flexibility. It can be applied across various qualitative data sets and is not tied to a specific theoretical framework, making it particularly suitable for the interdisciplinary nature of UX research. This method enables researchers to drill down into the qualitative data, moving beyond surface-level observations to uncover underlying user needs, behaviors, and attitudes.

Moreover, thematic analysis is valuable in UX research for its emphasis on the iterative process. As themes are developed and refined, researchers may return to the data multiple times. This iterative nature ensures a deep engagement with the data, allowing for a thorough exploration of its complexities.
In UX research, the output of thematic analysis—clearly defined and well-interpreted themes—can be linked to actionable insights that can directly inform design decisions. It helps to answer not just what users are doing, but why they are doing it, offering a deeper understanding of their experiences. These insights can guide improvements in product design, interface layout, and overall user experience, ensuring that products are more closely aligned with user needs and expectations.
By employing thematic analysis, researchers can systematically dissect and interpret qualitative data, turning it into meaningful insights that drive user-centered design and strategy. This method offers a structured yet flexible approach to uncovering the rich, detailed perspectives of users, making it an indispensable method in the arsenal of UX research techniques.
When should you do thematic analysis in UX research?
Deciding when to employ thematic analysis in user experience (UX) research is pivotal for extracting actionable insights from qualitative data. This analytical method is particularly useful in various contexts, each justifying its application to enhance understanding and decision-making in UX design and strategy.
Whether it's uncovering the nuanced needs and preferences of users, improving the usability and overall experience of a product, or guiding the direction of product development and innovation, thematic analysis serves as a critical method.
This section looks at three specific scenarios where thematic analysis proves indispensable: identifying user needs and preferences, enhancing usability and user experience, and informing product development and innovation. In each, we'll explore how thematic analysis can transform raw data into meaningful themes that drive targeted and effective UX strategies.
Identifying user needs and preferences
Thematic analysis is invaluable when the goal is to deeply understand the needs, preferences, and experiences of users. Through careful examination of qualitative data, such as interview transcripts and open-ended survey responses, thematic analysis reveals patterns that signify what users find important, frustrating, or desirable in a product or service.
These insights are crucial for creating or improving offerings that genuinely resonate with the target audience. By bringing user needs and preferences to the forefront, thematic analysis ensures that design decisions are grounded in real user feedback, thereby enhancing the relevance and appeal of the product.

Improving usability and user experience
Another critical juncture for thematic analysis is in the evaluation and enhancement of product usability and user experience. This method allows researchers to sift through user feedback, identifying common themes related to usability challenges or aspects of the product that users particularly enjoy.
Such themes can then inform targeted improvements, making products more intuitive, accessible, and enjoyable for users. Thematic analysis not only highlights areas for refinement but also helps validate design changes by tracking themes in user feedback over time, ensuring that revisions truly address user needs.
Guiding product development and innovation
Finally, thematic analysis plays a pivotal role in steering product development and fostering innovation. By analyzing qualitative data for emergent themes, companies can uncover gaps in the market, anticipate user needs, and identify opportunities for new features or products.
This approach is particularly effective in revealing emerging trends and user behaviors that quantitative data alone might overlook. Incorporating these insights into product development strategies can lead to more innovative solutions that meet the evolving needs of users, positioning companies as leaders in their respective fields.

The thematic analysis process for UX research
The thematic analysis process in UX research is a methodical approach designed to uncover patterns and insights from qualitative data, offering a deeper understanding of user experiences. This process involves several key steps, each building upon the last to ensure a comprehensive analysis of the data collected from user interactions.
Starting with an intimate familiarity with the data, moving through the generation of initial codes, and culminating in the crafting of a detailed report, this process enables UX researchers to transform raw data into actionable insights. Below, we outline the major steps involved in thematic analysis specific to UX research, guiding researchers through a structured approach to qualitative analysis.
Familiarizing yourself with the data
The first step in the thematic analysis process involves immersing oneself in the data collected from various UX research methods, such as interviews, focus groups, and user testing sessions. This phase requires reading through all the data meticulously, watching any recordings, and taking notes of initial impressions, thoughts, and potential patterns.
This thorough engagement with the data is critical for developing an intuitive understanding of what users have expressed, setting the stage for more structured analysis. It enables researchers to identify key ideas and issues that may become central to the later stages of analysis.
Generating initial codes
Following the initial review, the next step is systematically coding the data. This involves segmenting the text (or other data forms) and applying concise labels (codes) that capture the essence of each segment related to user experience.
Coding is a flexible process, allowing for both inductive codes, which emerge from the data itself, and deductive codes, which are based on pre-existing concepts or theoretical frameworks. This step organizes the data into manageable pieces, making it easier to identify patterns and themes in the subsequent stages of analysis.
Searching for themes
With a comprehensive set of codes in place, the analysis progresses by sorting these codes into potential themes. This process entails grouping codes that share similar concepts or narratives into clusters that reflect broader patterns across the data.
Searching for themes is a creative and iterative process, often requiring the researcher to go back and forth between the dataset and the emerging themes to refine and adjust the grouping. This step is pivotal as it transforms the organized data into meaningful insights about the user experience, laying the groundwork for deeper analysis and interpretation in the later stages.
Reviewing themes
After identifying potential themes, the next step is to review and refine them to ensure they accurately represent the data. This involves a critical evaluation of each theme, examining its coherence and its ability to capture the essence of the dataset.
Researchers may find it necessary to split, combine, or discard themes during this phase to better align with the data insights. Reviewing themes often requires returning to the dataset to verify that the themes genuinely reflect the coded data and adjusting the coding scheme as needed.
This iterative process ensures that the developed themes are robust, distinct, and meaningful, providing a clear and meaningful reflection of the user experiences captured in the data.
Defining and naming themes
Once the themes have been refined, the focus shifts to defining and naming them. This step is crucial for articulating the core idea of each theme and explaining how it contributes to understanding the user experience.
A clear definition includes a detailed description of what the theme encompasses and how it relates to the research questions and objectives. Naming each theme involves choosing a term or short phrase that captures its essence, making the themes easily recognizable and understandable.
This clarity is essential for communicating the findings effectively, both within the research report and in discussions with stakeholders.
Writing the report
The final step in the thematic analysis process is drafting the report. This document synthesizes the analysis, presenting the themes in a structured and coherent manner.
It includes an overview of the methodology, a detailed description of each theme, and examples from the data to illustrate the themes. The report should also discuss the implications of the findings for UX design and strategy, highlighting how the themes inform user needs, preferences, and potential areas for improvement.
Writing the report is an opportunity to convey the depth and breadth of the insights gained through the thematic analysis, offering actionable recommendations based on a nuanced understanding of the user experience.

Challenges in analyzing UX research data
Analyzing UX research data presents a unique set of challenges that can impact the quality and effectiveness of the findings. Whether dealing with the vast diversity of user interactions, the complexity of qualitative data, or the nuances of user behavior, researchers must navigate these hurdles with skill and insight.
This section explores four key challenges encountered in the analysis process: managing large volumes of data, ensuring high-quality findings, interpreting complex qualitative data, and integrating findings into actionable design recommendations. Understanding these challenges is crucial for researchers aiming to derive meaningful insights that can genuinely enhance user experience and guide design improvements.
Managing large volumes of data
One of the primary challenges in analyzing UX research data is managing the sheer volume of information collected from various sources such as interviews, surveys, and usability tests. The abundance of data can be overwhelming, making it difficult to organize and sift through to find relevant insights.
Researchers must employ meticulous data management strategies, including the use of coding in thematic analysis, to systematically categorize and analyze the data. Effective data management requires not only a well-planned approach but also tools and software designed for qualitative data analysis. Without these, there's a risk of missing critical insights or becoming bogged down in data that is not actionable.

Ensuring high-quality findings
Ensuring that the analysis of UX research data is rigorous and credible can be a significant challenge. It is important to convey consistency of the analysis process and its findings as well as credibility that the findings are grounded in the data and user experiences.
Achieving these requires rigorous methodological approaches, including clear criteria for data coding and theme development and transparent descriptions of the entire analysis process.
Researchers must also remain vigilant against implicit assumptions that could skew the analysis, ensuring that interpretations are supported by the data. Balancing reflexive subjectivity with systematic analysis techniques is key to producing findings that meaningfully represent user experiences and can inform design decisions effectively.
Interpreting complex qualitative data
Interpreting complex qualitative data is another significant challenge in UX research. This type of data often contains nuanced details about user behaviors, attitudes, and emotions, which can be difficult to distill into clear, actionable insights.
The complexity arises from the varied ways users express themselves, the subtleties of language, and the context-dependent nature of their feedback. Researchers must navigate this complexity by employing a deep understanding of the subject matter, a keen sense of empathy, and a rigorous analytical framework to interpret the data.
This involves looking beyond the obvious to uncover underlying themes and patterns that can inform design improvements. The risk here is oversimplification or misinterpretation of the data, which can lead to misguided design decisions.
Integrating findings into actionable design recommendations
Another key challenge in analyzing UX research data is translating the insights gained into actionable design recommendations. This step requires not only a thorough understanding of the analysis but also creativity and strategic thinking to envision how the findings can be applied to enhance the product or service.
Researchers must bridge the gap between abstract themes and concrete design actions, making sure recommendations are both feasible and aligned with project goals. This often involves collaboration with designers, developers, and other stakeholders to ensure the insights are implemented effectively.
Overcoming this challenge is crucial for ensuring that the research has a tangible impact on improving user experience, making it one of the most important aspects of UX research.