- What is Thematic Analysis?
- Advantages of Thematic Analysis
- Disadvantages of Thematic Analysis
- Thematic Analysis Examples
- How to Do Thematic Analysis
- Thematic Coding
- Collaborative Thematic Analysis
- Thematic Analysis Software
- Thematic Analysis in Mixed Methods Approach
- Abductive Thematic Analysis
- Deductive Thematic Analysis
- Inductive Thematic Analysis
- Reflexive Thematic Analysis
- Thematic Analysis in Observations
- Thematic Analysis in Surveys
- Thematic Analysis for Interviews
- Thematic Analysis for Focus Groups
- Thematic Analysis for Case Studies
- Thematic Analysis of Secondary Data
- Thematic Analysis Literature Review
- Thematic Analysis vs. Phenomenology
- Thematic vs. Content Analysis
- Thematic Analysis vs. Grounded Theory
- Thematic Analysis vs. Narrative Analysis
- Thematic Analysis vs. Discourse Analysis
- Thematic Analysis vs. Framework Analysis
- Thematic Analysis in Social Work
- Thematic Analysis in Psychology
- Thematic Analysis in Educational Research
- Thematic Analysis in UX Research
- How to Present Thematic Analysis Results
- Increasing Rigor in Thematic Analysis
- Peer Review in Thematic Analysis
- How to cite "The Guide to Thematic Analysis"
How to Present Thematic Analysis Results
Presenting thematic analysis results effectively is a crucial step in communicating how you were able to identify patterns clearly and concisely. Thematic analysis, widely used among qualitative research methods, involves identifying, analyzing, and reviewing themes within qualitative data. When presented well, the findings from a thematic analysis can identify themes that emerge from the data, offering valuable insights into the research question. In this article, we will outline the steps and strategies for presenting the results of a thematic analysis in research papers. Our focus will be on clarity, organization, and the effective communication of your findings to your audience. By adhering to these guidelines, researchers can ensure that their thematic analysis results are understood and appreciated by readers, thereby enhancing the impact of their research.

How do you present a thematic analysis?
Presenting a thematic analysis involves more than just listing the themes identified during your research. It is about constructing a coherent narrative that effectively communicates the essence of your data to the audience. This section of your paper should clearly articulate how each theme relates to your research question, providing depth and insight into your analysis. The upcoming subsections will guide you through organizing your themes, elaborating and supporting them with data, and employing visual aids for enhanced clarity.
Organizing your themes
Organizing your themes is a critical step in the effective presentation of your thematic analysis, ensuring that your findings are conveyed with clarity and impact. The organization process involves creating a structured framework where themes are categorized and related in a manner that reflects the narrative of your research.
To start, establish a hierarchy where main themes represent broad, overarching categories, with sub-themes from revised initial codes providing more detail and specificity nested within them. This hierarchy is not just about structure; it's about creating an intuitive map of your data that showcases the relationships between different aspects of your findings.
Next, consider the sequence in which you present your themes. This should not be arbitrary; it should tell the story of your data in a way that is logical and impactful, whether it aligns chronologically, by significance, or in relation to your research questions. A well-thought-out sequence helps in guiding your audience through your analysis smoothly, ensuring that they grasp the flow of your argumentation.
Consistency is key in the presentation of your themes. Ensure that the way you describe and refer to each theme remains uniform throughout your analysis, with clear and descriptive labels that capture the essence of the data they represent. This consistency aids comprehension, making it easier for your audience to follow and engage with your findings.
Finally, elucidate the interconnections between themes, illustrating how they interweave and contribute to the overarching narrative. Providing this context not only enriches your analysis but also underscores the relevance and significance of each theme, offering a deeper insight into your research question.
Through careful organization, you provide a clear and insightful framework that enhances the presentation of your thematic analysis, allowing your audience to fully grasp and appreciate the depth of your research findings.
Describing and supporting your themes
In presenting your thematic analysis, it is crucial to describe and support your themes thoroughly to provide a robust and credible account of your findings. This involves a detailed explanation of each theme, supplemented by evidence from your data, which collectively anchors your analysis in the empirical world.
When describing your themes, aim for clarity and depth. Each theme should be articulated with precision, outlining its scope and dimensions. This description should go beyond mere labels, delving into the nuances and variations within each theme. It is essential to convey the richness and complexity of the data, presenting a vivid picture that captures the essence of the theme.
Supporting your themes with data is equally important. This involves selecting and presenting excerpts from the relevant data, as well as the individual codes and categories that exemplify and substantiate each theme. These data extracts should be chosen carefully to illustrate the theme's prevalence and significance within your dataset. They serve as concrete evidence that grounds your thematic interpretation, enabling readers to see the connection between your analytical insights and the raw data.
Furthermore, it is important to contextualize these themes within the broader landscape of your research. This includes discussing how each theme relates to your research questions and objectives, as well as situating them within existing literature and theoretical frameworks. From a methodological approach, describing every stage of the analysis process from initial coding of the data to validation of themes will provide the necessary research rigor for your study. Such contextualization not only reinforces the quality of your analysis but also demonstrates its relevance and contribution to the field.
By thoroughly describing and supporting your themes, you strengthen the credibility and persuasiveness of your thematic analysis. This approach not only enhances the transparency of your research process but also allows readers to engage deeply with your findings, appreciating the rigor and insight of your analysis.

Visualizing data for clarity
Data visualizations are a powerful tool in presenting thematic analysis results, offering a clear and impactful way to communicate complex information. Through effective visualization, you can enhance the comprehensibility and appeal of your findings, allowing readers to grasp the essence of your analysis at a glance.
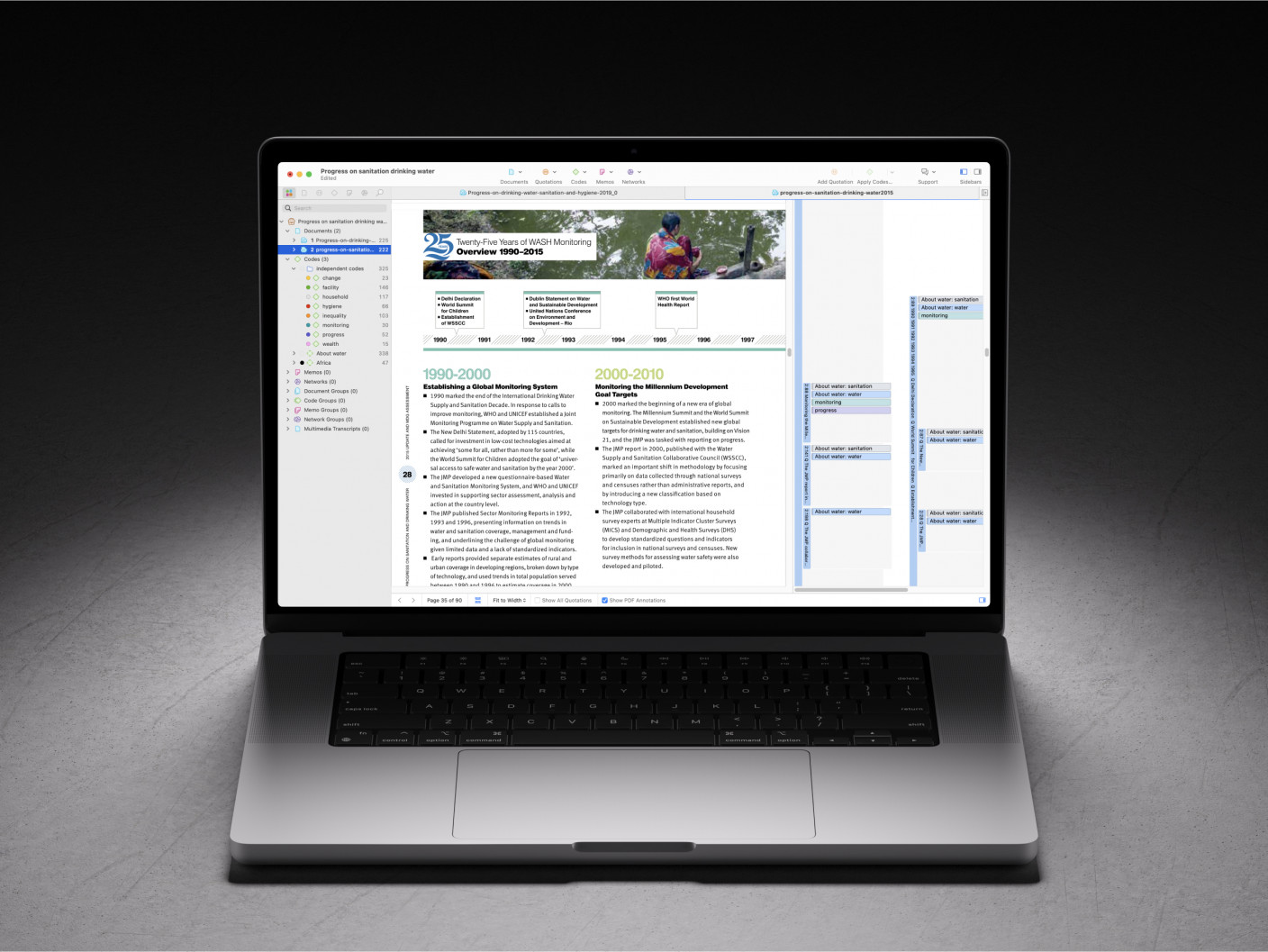
Effective data visualization in thematic analysis typically involves the use of thematic maps or charts that illustrate the relationships and hierarchies among identified themes. For example, a thematic map can display how various sub-themes branch out from main themes, highlighting the interconnections and the relative importance of each theme. These visual elements should be designed with clarity and simplicity in mind, ensuring that they complement the text without overwhelming the reader.
In addition to thematic maps, other visual tools like bar charts, tables, or Sankey diagrams can be employed to depict the frequency or distribution of themes within the data set. Such quantitative visualizations can provide a straightforward representation of the prevalence of certain themes, lending empirical weight to qualitative insights.
When incorporating visual elements into your thematic analysis presentation, it is crucial to maintain consistency in style, color, and formatting. This consistency aids in reader comprehension and reinforces the cohesion of your overall analysis. Furthermore, each visual display should be clearly labeled and accompanied by a descriptive caption that elucidates its relevance and key takeaways.
Lastly, it is essential to ensure that your visualizations are accessible to all readers, including those with visual impairments. This can be achieved by choosing color schemes with sufficient contrast and providing text descriptions for visual content.
By integrating clear and meaningful visualizations into your thematic analysis presentation, you can illuminate the structure and significance of your themes, enhancing the overall clarity and impact of your findings.