Research tools for qualitative data analysis
- Introduction
- What is research software?
- How can software make research easier?
- Types of research software
- How to choose the right software package
- What makes the best qualitative research software?
Introduction
Research software and tools can significantly streamline the process of conducting studies for academic research, scientific research, and commercial research, from planning and data collection to analysis and presentation of findings.
These tools provide features that help researchers stay organized, manage large datasets, and efficiently analyze information. With the growing range of software options available, each catering to specific research needs, understanding what these tools offer and how they can be used effectively becomes essential.
This article provides an overview of different types of research software, their benefits, and practical considerations for choosing the right tools for your project. It will also cover what to look for when selecting qualitative research software to ensure it meets your specific requirements.
What is research software?
Research software includes various digital tools designed to support different stages of the research process. These tools assist researchers in planning studies, collecting and managing data, analyzing results, and presenting findings in a structured manner.
Depending on the research type and methodology, software options can range from specialized qualitative data analysis tools to quantitative statistical packages, as well as general-purpose tools for managing literature, references, and writing.
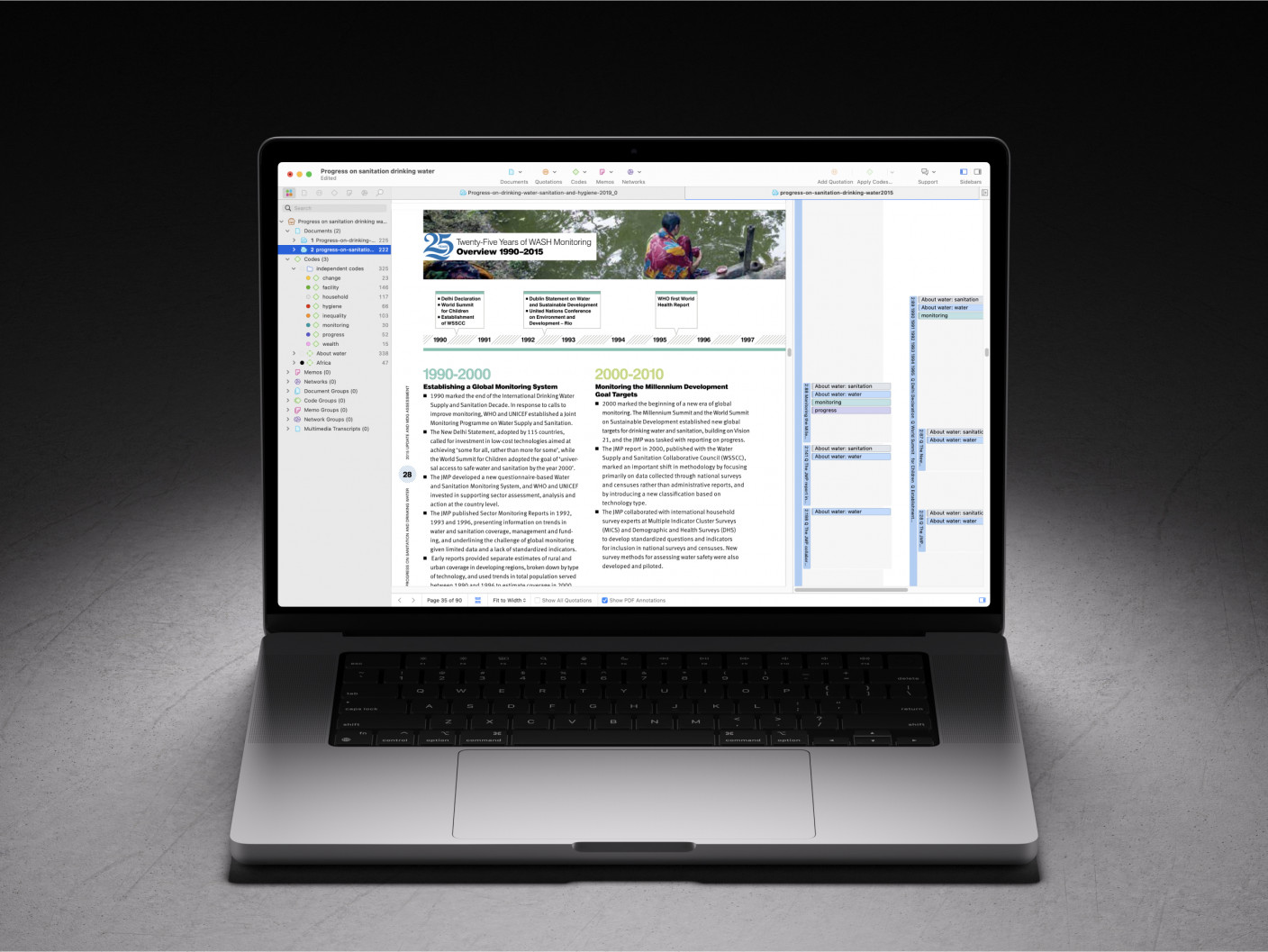
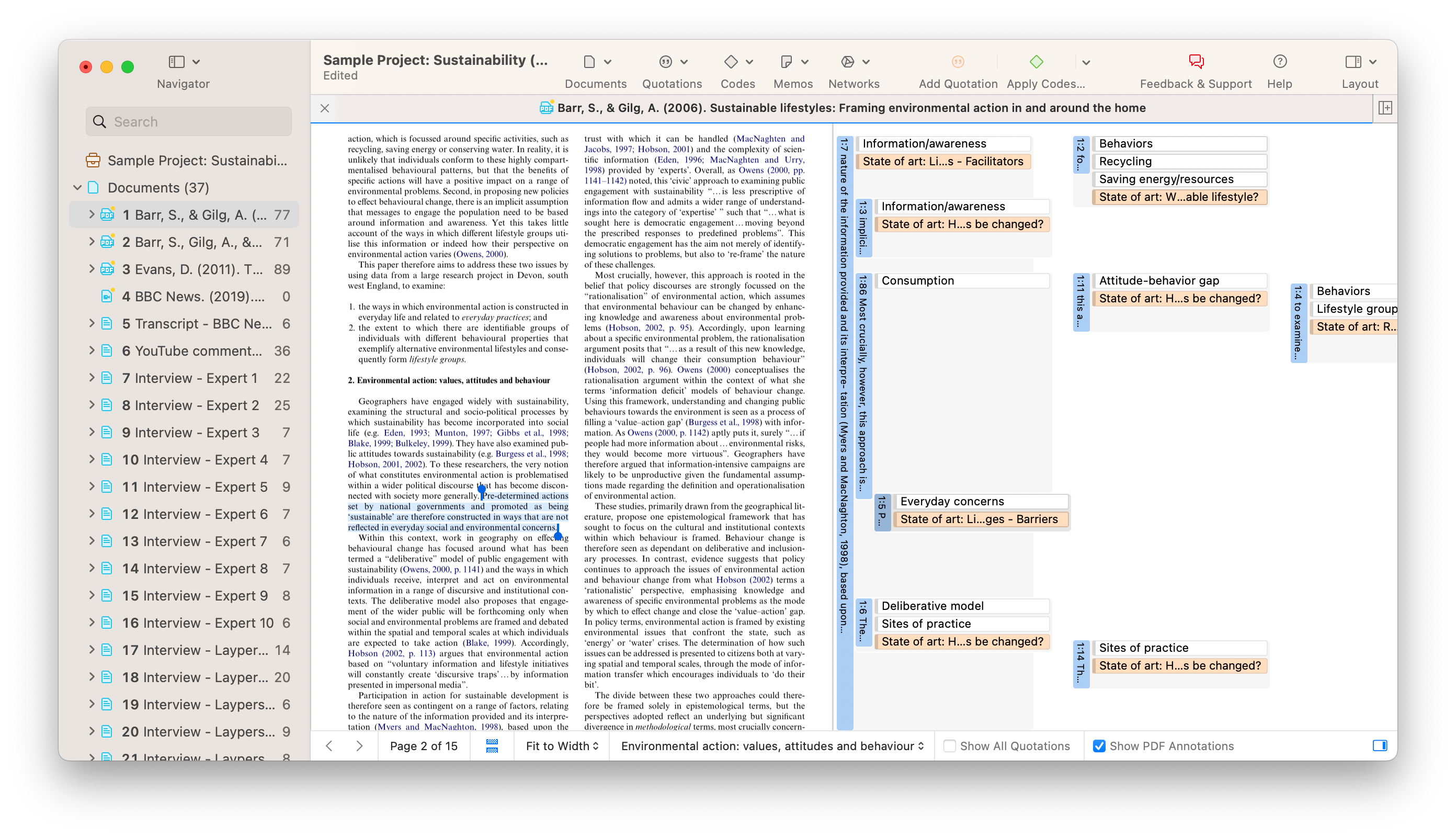
Qualitative research software, such as ATLAS.ti, focuses on helping researchers manage and analyze non-numerical data like interviews, open-ended survey responses, and observations. These tools offer features such as coding, memoing, and visualizing data relationships, making it easier to identify patterns and themes.
Quantitative research software, like SPSS, Stata, and R, primarily deals with numerical data, supporting tasks like statistical analysis, data visualization, and hypothesis testing. These tools can assist in analyzing datasets that require complex statistical operations, including regressions, t-tests, and other advanced techniques.
Beyond analysis-specific tools, there is also software designed to aid in other research tasks. Reference management tools like EndNote, Mendeley, and Zotero help organize and cite sources effectively. Writing tools, including Scrivener or Microsoft Word, offer features that facilitate drafting, structuring, and formatting research documents.
Overall, research software aims to enhance the efficiency and quality of the research process by reducing manual tasks and providing robust analytical capabilities. As research becomes increasingly complex and data-driven, the use of such software has become a critical part of ensuring that studies are conducted methodically and findings are presented clearly.
Understanding the different types of software available helps researchers choose tools that best meet their specific needs and research goals.

How can software make research easier?
Research software can greatly simplify various aspects involved in conducting research, from the initial planning stages to the final presentation of results. These tools provide structured ways to handle data, organize thoughts, and conduct analysis, which saves time and minimizes errors.
By taking advantage of specific functionalities, researchers can enhance their productivity and focus on the most critical aspects of their work. Below are several ways software can streamline research tasks.
Plan research
Research software can assist in planning by providing frameworks and templates to develop research designs, outline methodologies, and establish data collection strategies. Researchers can collect literature from places like Google Scholar or Academia, a social networking site designed for sharing research, and organize previous studies in research software for their literature review.
Then, tools like Microsoft Project or Trello help organize tasks, set deadlines, and manage resources efficiently. For qualitative research, software like ATLAS.ti offers planning features that allow researchers to map out their coding schemes and data collection protocols in advance, ensuring consistency throughout the study.
Collect data
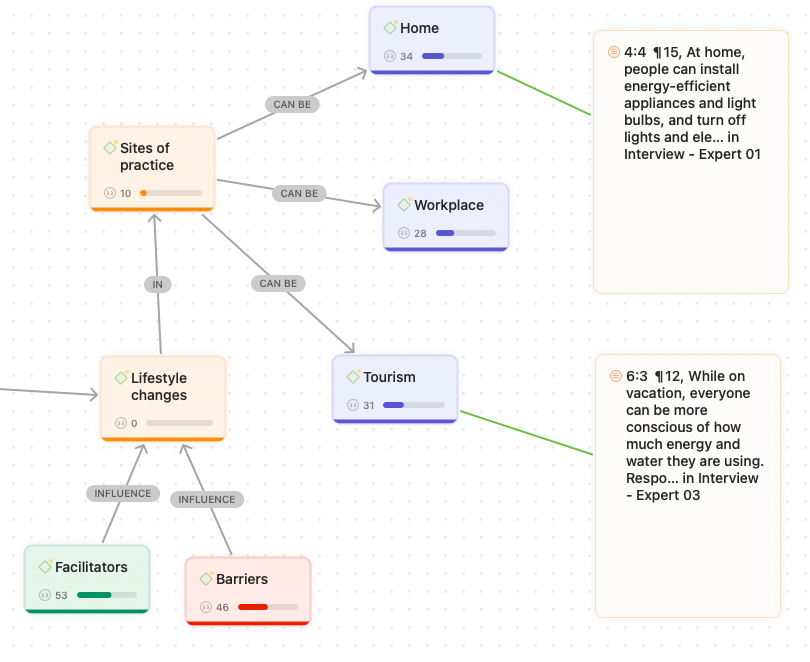
Data collection can be one of the most time-consuming parts of research. Software tools help automate and simplify the process of gathering research materials. For qualitative studies, software such ATLAS.ti allows for the direct importation of data from various sources like interviews, focus groups, or online surveys.
For quantitative research, tools like REDCap or Qualtrics facilitate data collection by providing secure platforms for survey administration, automatic data entry, and validation checks to ensure data integrity. These tools reduce the manual effort involved in data entry and help minimize errors, making data collection more efficient and reliable.
Organize data
Once all the data is collected, research software can help organize it in a way that makes it easy to access and use. Qualitative research software offers features for tagging, coding, and categorizing data, which helps researchers keep track of themes and patterns as they emerge.
Quantitative tools provide data management features that allow researchers to sort, filter, and structure large datasets for analysis. Tools like Evernote or OneNote can also be used to organize notes, references, and other materials related to the research, ensuring everything is easily accessible and well-organized. Effective data organization reduces the risk of losing important information and makes the analysis phase more manageable.
Analyze data
Analyzing data is a central component of research, and software tools can significantly enhance this process by offering powerful analytical capabilities. For qualitative research, software like ATLAS.ti allows researchers to code text, audio, and video data systematically, facilitating thematic analysis and the identification of patterns and trends.
Quantitative research software, such as SPSS, R, or Stata, provides advanced statistical tools for data analysis, including regression analysis, ANOVA, and hypothesis testing. These tools often come with built-in visualization features that help researchers interpret their findings. By automating complex calculations and analyses, these tools save time and increase accuracy, enabling researchers to draw meaningful conclusions from their data more efficiently.
Reflect on insights
Reflecting on insights provides pathways for exploring the implications of research findings. Research software often includes tools that allow researchers to document their reflections, thoughts, and interpretations throughout the research process.
Memoing features in qualitative research software, like those in ATLAS.ti, enable researchers to write notes and reflections directly within the software, linking them to specific data points or codes. This function supports a continuous process of reflection and helps maintain a clear trail of how insights were developed over time. By facilitating this reflective practice, research software helps researchers ensure their interpretations are transparent and grounded in the data.
Visualize results
Presenting research findings clearly and effectively is essential for communicating their significance in academic papers or presentations. Research software often includes visualization tools that help transform complex data into understandable formats, such as charts, graphs, word clouds, or conceptual maps. Qualitative research tools offer features to create visual representations of themes and patterns, while quantitative tools provide options for generating statistical graphs and plots.
Tools like Tableau or Microsoft Power BI provide advanced data visualization capabilities that can be used to create interactive dashboards and visual presentations. Visualizations not only enhance the readability of research findings but also help uncover patterns and relationships in the data that may not be immediately apparent through text alone.
Types of research software
Research software comes in various forms, each designed to support different aspects of the research process. Depending on the nature of the study and the researcher's needs, the choice of software can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of the research. Here are the primary types of research software commonly used.
Qualitative research software
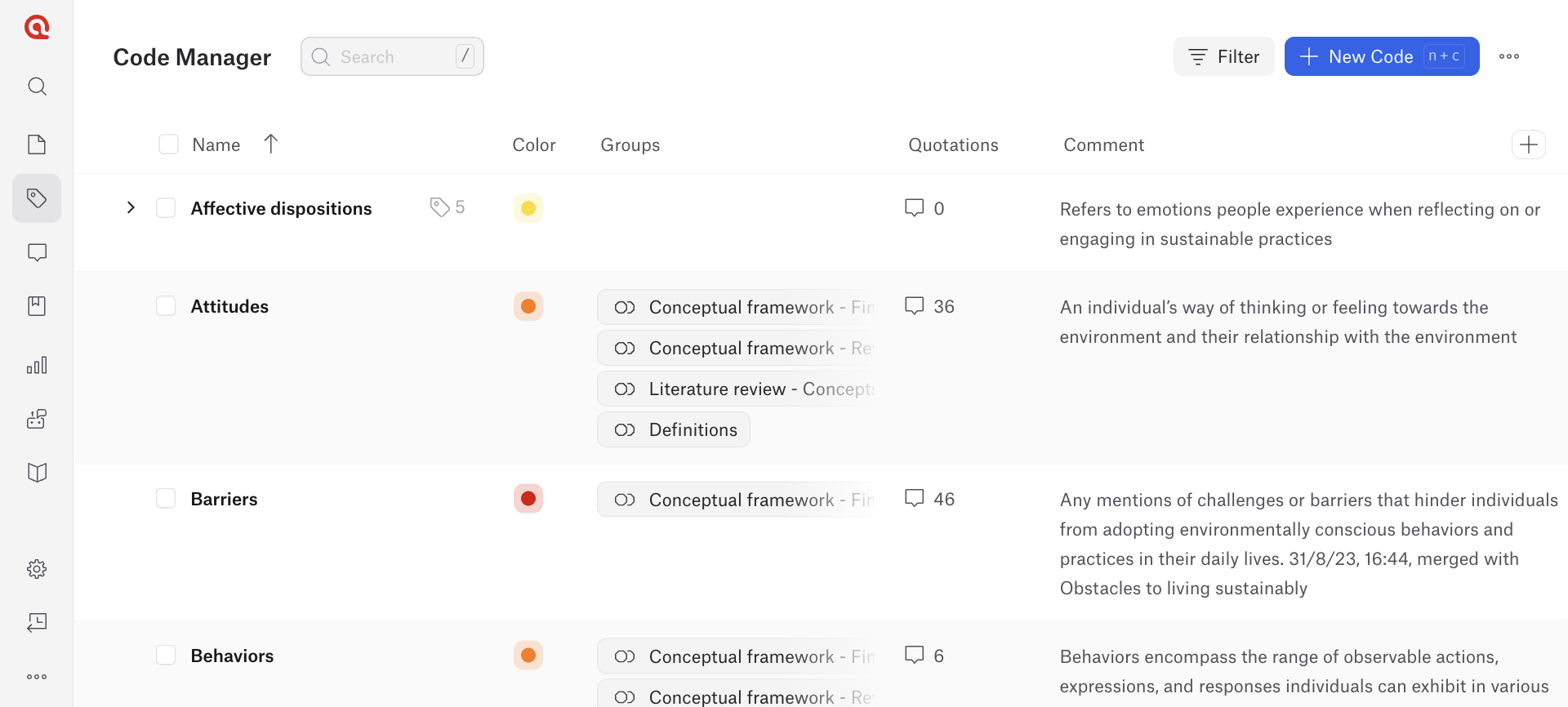
Qualitative research software is tailored to analyze non-numerical data, such as interviews, focus groups, open-ended survey responses, and observations. Tools like those found in ATLAS.ti offer a range of features to facilitate the management, coding, and analysis of qualitative data. These programs allow researchers to systematically code text, images, audio, and video data, helping to identify patterns and themes across different data sources.
They also provide features for memoing, linking data points, and visualizing relationships through mind maps or network diagrams, which supports a deeper understanding of complex datasets. By using proprietary software for qualitative research, researchers can streamline data handling, enhance the transparency of their analysis process, and conduct rigorous research.

Quantitative research software
Quantitative research software is designed for analyzing numerical data and performing statistical analysis. Common tools in this category include SPSS, Stata, R, and SAS. These programs offer a wide range of statistical functions, from basic descriptive statistics to advanced modeling techniques like regression analysis, multivariate analysis, and machine learning algorithms.
They also provide data management capabilities, enabling researchers to clean, merge, and manipulate large datasets efficiently. Many quantitative tools come with built-in or customizable scripts for automating repetitive tasks, which reduces manual work and helps ensure accuracy. The software's robust analytical functions are essential for interpreting data, testing hypotheses, and drawing meaningful conclusions from complex numerical datasets.
Software for writing research
Software for writing research is designed to assist researchers in drafting, organizing, and managing their written outputs, such as research papers, theses, or dissertations. Tools like Microsoft Word, Scrivener, and LaTeX provide a range of features for text formatting, citation management, and document structuring. These programs help researchers maintain consistency in style and format, which is especially important when adhering to specific publication or academic guidelines.
Additionally, reference management software like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley can integrate with writing tools to automate citation insertion and bibliography creation, saving time and reducing errors. By streamlining the writing and referencing process, these tools allow researchers to focus on content development and refinement.
How to choose the right software package
Choosing the right software for research can be challenging, given the wide range of available options. The right choice depends on several factors, including the research type, the project's specific needs, the research team's skills, and budget constraints. Here are three key considerations to help guide the selection process.
Determine the research needs
The first step in selecting a software package is to define the specific needs of your research project. Consider the type of data you will collect and analyze, the methodologies you plan to use, and the end goals of your research.
For instance, if your study involves qualitative data like interviews or open-ended survey responses, qualitative research software such as ATLAS.ti would be most appropriate. If your research requires statistical analysis of numerical data, a quantitative tool like SPSS or R would be more suitable.
Additionally, think about the scope and scale of your project. If you are working on a large-scale study that involves multiple team members, look for software that supports collaboration, version control, and secure data sharing.
On the other hand, if your research is a small, solo project, simpler tools may suffice. Clearly understanding your research needs will help you narrow down the software options that provide the most relevant features.
Assess the ease of use and support
Another critical factor in choosing research software is its ease of use. Consider the technical skills required to use the software effectively and whether your team has those skills. Some tools, like Microsoft Word or SPSS, are widely used and relatively straightforward, requiring minimal training.
Others, such as R or LaTeX, may offer more advanced features but come with a steeper learning curve and may require training or prior experience.
Look for software that offers a balance between functionality and usability for your team. Check if the software provides comprehensive documentation, tutorials, or user support forums to help new users get started.
Also, consider whether the software has an active community of users who can offer tips, advice, and troubleshooting support. Tools with strong support networks and resources will likely be easier to implement and use effectively over the long term.
Consider budget and compatibility
Budget is a key consideration when choosing research software. Prices can range from free, open-source options to expensive, subscription-based packages. Determine how much you are willing to spend and explore software that fits within your budget.
Free or open-source tools like Zotero or R can be excellent choices for researchers with limited funds, while subscription-based tools like Tableau or SPSS might offer more comprehensive features and support.
Additionally, consider compatibility with your existing systems and workflows. Ensure the software integrates well with other tools you are already using, such as reference managers, data storage solutions, or writing tools.
Compatibility helps maintain a smooth workflow and reduces the need for time-consuming manual data transfers or reformatting. Check for software that is available on multiple platforms (e.g., Windows, macOS, Linux) if you or your team members use different operating systems. Ensuring compatibility will help prevent technical issues and streamline the research process.

What makes the best qualitative research software?
Choosing the best qualitative research software involves considering several key factors that directly impact the research process. The ideal software should support efficient data management, offer robust analysis tools, and enhance collaboration and flexibility.
Here are four essential aspects to consider when selecting qualitative research software.
User-friendly interface
An intuitive interface is essential for effective qualitative research software. The software should be intuitive and easy to navigate, minimizing the learning curve for new users and allowing researchers to focus more on their data rather than on figuring out how to use the tool.
Features like drag-and-drop functionality, customizable workspaces, and straightforward menu layouts contribute to an accessible user experience. Software packages like ATLAS.ti, known for its clear interface, also offer tutorials, help guides, and community support, further easing the onboarding process. An accessible and easy-to-use tool for research ensures that researchers, regardless of their technical skills, can effectively use the software to manage and analyze their data.
Comprehensive data management
Effective data management is a cornerstone of qualitative research. The best software provides robust tools for importing, organizing, and storing various types of data, including text, audio, video, and images. It should support flexible coding systems that allow for easy categorization and retrieval of data.
ATLAS.ti offers advanced data management features, such as automatic data backup, hierarchical coding structures, and the ability to link multiple data points for cross-referencing. Additionally, strong search and query capabilities enable researchers to quickly find specific data or identify patterns across datasets. Comprehensive data management tools help maintain the integrity of the research data and ensure that all relevant information is accessible throughout the analysis.
Versatile analysis tools
Versatile analysis tools are essential for qualitative research, where data interpretation often involves multiple approaches. The best software should provide a range of features conducive to qualitative analysis, such as thematic coding, text analysis, sentiment analysis, and visualization options. For instance, ATLAS.ti provides word frequency analysis, coding queries, and network views to restructure data or visualize relationships between different data points.
The software should also allow for mixed methods research, combining qualitative and quantitative analysis within the same platform. Versatile analysis tools enable researchers to explore their data from various angles, enhancing the depth and richness of their findings.
Collaboration and data security
In collaborative research environments, the ability to share data and collaborate effectively is critical. The best qualitative research software should facilitate team collaboration through features like version control, real-time updates, and secure data sharing. ATLAS.ti provides such a cloud-based platform where multiple researchers can work on the same project simultaneously, track changes, and communicate within the software.
Additionally, data security is a paramount concern, particularly when dealing with sensitive information. Look for software that offers strong encryption, user authentication, and compliance with data protection regulations like GDPR. Ensuring both collaboration capabilities and robust data security helps maintain the integrity of the research process and protects participant privacy.